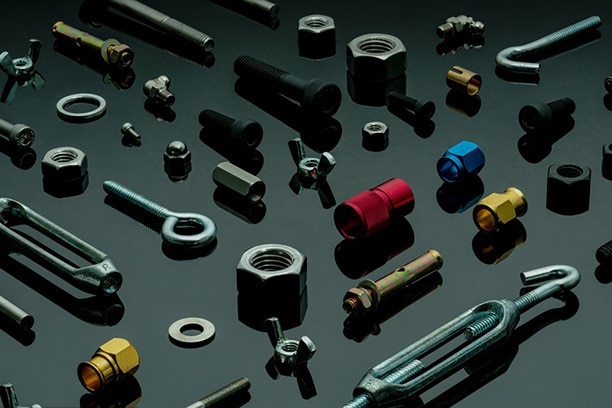
Within the realm of mechanical engineering, numerous types of fasteners are employed for assembling CNC machined components, structures, and diverse connections. The critical question is how to recognize an extensive array of fasteners and determine the appropriate one for particular applications. In this article, we are going to examine various fasteners and explore the distinctions among bolts, nuts, screws, and rivets.
Introduction to Common Types of Fasteners
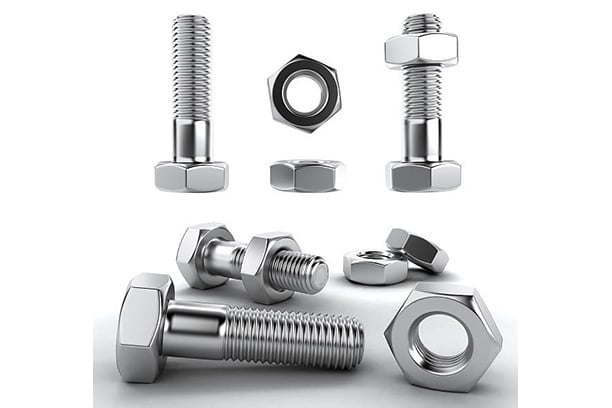
What Are Bolts?
A bolt, a threaded cylindrical rod, also serves as a fastener. Its grooves fit perfectly with the nut’s, creating a secure joint due to the combination of their thread frictions.
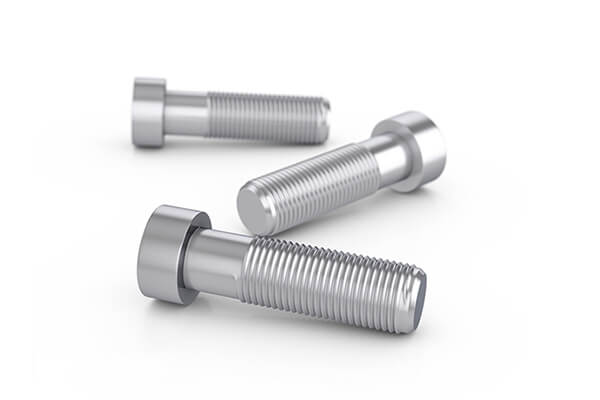

Features of Bolts:
- A bolt has external threading and can be either fully or partially threaded.
- Bolts are cylindrical in form, consisting of a solid cylinder with a head, known as the shank.
- The size of a bolt is generally larger than that of a nut.
- Bolts undergo tensile forces, which can ultimately cause them to fail.
- There are multiple types of bolts, including Machine bolts, T-head bolts, Toggle bolts, U-bolts, J-bolts, Eye bolts, Plow bolts, Anchor bolts, Carriage bolts, Elevator bolts, Shoulder bolts, Square head bolts, Stud bolts, Flange bolts, Hanger bolts, Hexagon bolts/Tap bolts, Lag bolts, Timber bolts, etc.
What Are Nuts?
Nuts are a type of fastener with a threaded hole that is typically used in conjunction with bolts to connect two components. When combined with a bolt, the two partners (nut and bolt) are secured together by the friction of their threads, along with a slight stretching of the bolt and compression of the parts being joined.
Features of Nuts:
- The nuts come with an alternative locking mechanism that prevents loosening caused by vibrations from the machine components or the connected parts.
- They primarily have a circular cross-section.
- The nuts feature internal threads, allowing for effortless tightening onto the bolt.
- Their size is relatively smaller than the bolt it accompanies.
- Nuts undergo compressive forces, and it is this compressive stress that results in their failure.
- There is a wide variety of nuts, including Nylon insert lock nuts, Nylon insert jam lock nuts, Hex nuts, Jam nuts, Square nuts, Cap nuts, Acorn nuts, T-nuts, Kep nuts, Castle nuts, Flange nuts, Slotted nuts, Coupling nuts, Wing nuts, and among others.
What Are Screws?
Screws, similar to bolts, are fasteners with threads. However, they differ in that they may or may not have a head (e.g. set screws). They are typically used in pre-drilled holes or can tap their own hole while being installed. Unlike bolts, screws do not require a nut to secure them since they are tightened directly into the hole.
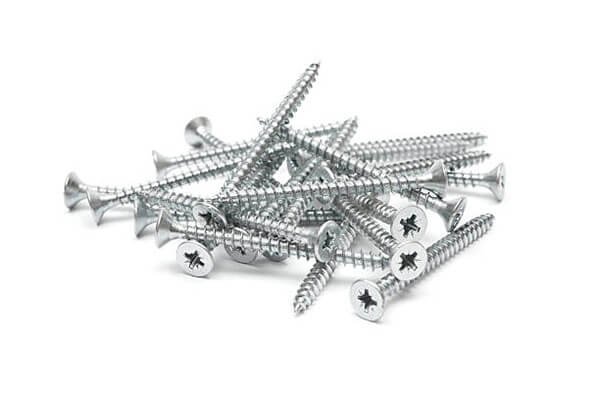

Features of Screws:
Screws differ from bolts as they have a tapered shaft, while bolts have a straight one. They are equipped with self-tapping or self-drilling points, making it easier to insert them without the need for pilot drill holes. Additionally, screws create a secure grip on the material through their threads, eliminating the need for nuts to tighten them. As a result, screws are typically shorter than the width of the material they are attached to. Screws are available in various sizes and thread types suitable for different applications involving metal, drywall, wood, and even concrete.
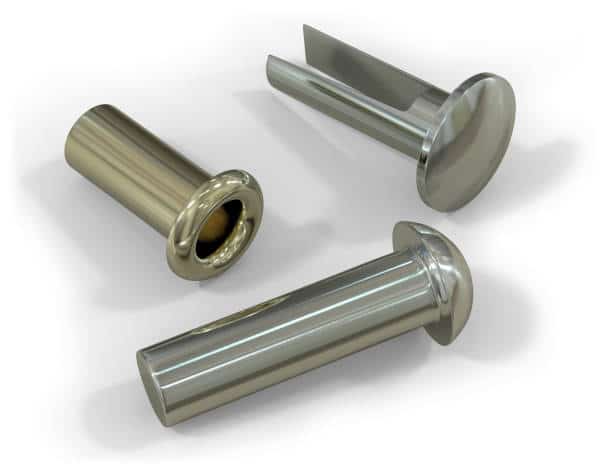
What Are Rivets?
Rivets, which are cylindrical in shape, are stationary mechanical tools with a head at the top, similar to bolts. Their purpose is to connect various parts together. Different varieties of rivets exist, such as solid and blind rivets. Solid rivets possess a solid shank with a head, while blind rivets are suitable for fastening applications where accessing the back of a workpiece is not feasible.
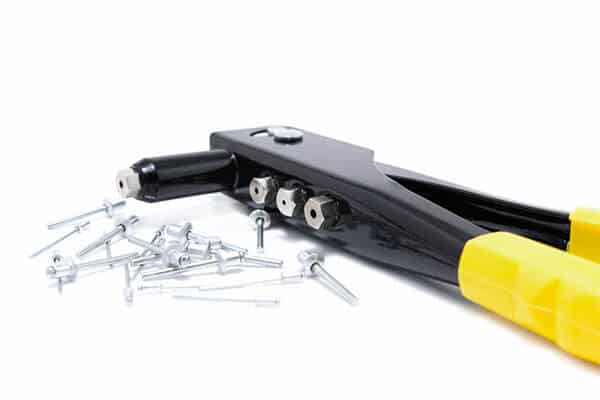

Features of Rivets:
- A type of fastener that has a head and tail at opposite sides is known as a rivet.
- Unlike threaded or nut-based fasteners, rivets are free from threads and nuts.
- Rivets are widely accepted as an irreversible process and can’t be undone once installed.
- The primary function of rivets as a type of joint is to provide a permanent assembly or connection of two or more parts.
- The removal of rivets can either be done through drilling or cutting them out.
Bolt vs Screw
Here, this chart outlines 7 primary characteristics that make bolts differ from screws:
| Characteristics | Bolt | Screw |
| Clamping Force | A nut and bolt assembly can create a high clamping force. | Screws are only used for low clamping force requirements. |
| Load Carrying Capability | Bolted joints have a very high reliability and can carry heavy loads. | Not available in larger sizes, screws have a lower load-carrying capability. |
| Size | Longer than the width of the parts through which it protrudes. | Often shorter than the width of the assembled components. |
| Shape | Uniform Shank | Non Uniform Shank |
| Uniform cross section | Can have a non-uniform cross- section | |
| Feature | A bolt requires nuts for securing. | Screws are self-sufficient. |
| The nut is subject to torque application. | Screwdrivers apply torque to screws. | |
| Used with Non-threaded components. | Can used with both threaded and unthreaded components. | |
| Installation | A spanner or other tools is usually required to fasten bolts. | Screws are tightened using a screwdriver or driver bit. |
| Cost | Bolted assemblies a more costly option. | Screws are a cheaper alternative. |
Learn more about our CNC Screw Machining Services
Bolt vs Rivet
The following chart compares bolts and rivets from 8 main features:
| Characteristics | Bolt | Rivet |
| Shape | A threaded shank and a head. | An unthreaded shank and a head. |
| Thread | Bolts have external threads that match that of a nut. | Free from threads and nuts. |
| Clamp load | Turning the nut and bolt is all that is required to create a high clamp load. | Due to their lack of threads, rivets are limited in their ability to create clamp loads. |
| Access | Access to both sides of the bolted joint is necessary for through-hole installation, but a tapped hole design can solve this issue. | It is possible to install from one side only, which is beneficial for applications with limited accessibility to the opposite side. |
| Tooling | Standard handheld tools | Specialized tooling |
| Vibration resistance | Nord-Lock washers can prevent bolts from loosening. | Due to vibration, the rivets will not rotate loose. |
| Reusability | Removal is quick and easy with standard tools, and parts can be reused. | Cutting out is necessary during removal, and the parts cannot be reused. |
| Installation | Simple and quick | Time-consuming |
Nut vs Bolt
The chart below lists main difference between nuts and bolts in terms of 7 aspects:
| Characteristics | Nut | Bolt |
| Shape | A nut is a cylindrical fastener with a hollow circular shape that is used with bolts. | Bolts are solid cylinders with a circular cross-section. |
| Nuts do not have heads. | Bolts have heads to tighten and loosen. | |
| A nut is a small metal object with a threaded hole. | A bolt has a cylindrical stem with threads at one end. | |
| The nut’s shape is a hexagon, making it easy and sturdy to hold from any side. | The bolt’s form is not hexagonal, as it has a single head connected to a long threaded shank. | |
| Material | Carbon steel coated with zinc. | High-grade steel containing a high percentage of nickel and chrome. |
| Force | Nuts are subject to compressive forces and often fail due to compressive stresses. | Bolts are subject to tensile forces and often fail due to tensile stresses. |
| Thread | Nuts have internal threads that match the threads of a bolt. | Bolts have external threads that match the threads of a nut. |
| Size | Nuts are typically smaller in size than bolts. | Bolts are generally larger in size than nuts. |
| Lock mechanism | Nuts have a locking mechanism to prevent loosening. | Bolts do not have any locking mechanism. |
| Variety | Castle Nut, Wingnut, T-Nut, Cape Nut. | J-Bolt, Lag Bolt, Toggle Bolt, U-Bolt. |
Rivet vs Screw
Machine screws and bolts are advantageous in easy disassembly and reassembly, the option to reuse the fastener, and the availability of fastening tools. Conversely, rivets offer resistance to vibration, low-profile heads, and rapid, low-cost assembly for large volumes of fasteners.
Rivets can be quickly installed to fit large volumes of fasteners in industrial machinery, making them an economical option. Moreover, they can be installed into blind holes, allowing for a solid bond without requiring access to the other side of the fastening surface. Lightweight and ideal for weight-critical applications, rivets are often used to fasten thin sheets without distorting them. This makes them ideal for assembling aircraft skins and military equipment.
Machine screws and bolts offer high strength, compatibility with commonly available tools, and easy disassembly and reassembly with fastener reuse. However, they have poor resistance to vibration, which is countered by vibration-resistant and locking nuts and thread locks.
Conclusion
This article discusses the key differences between common types of fasteners, namely bolts, nuts, screws, and rivets. Although these fastening components may seem similar at first glance, each one serves specific purposes and has distinct features. Bolts and nuts are designed to work together for secure joints, while screws function independently with their threaded shank and fasten materials by applying torque. Rivets, on the other hand, create strong and permanent joints when the rivet’s tail is deformed.
Understanding these differences enables us to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate fastener for a specific application, ensuring that structures and devices we create are reliable and built to last.
Custom CNC Machining Fasteners Manufacturer|Runsom Precision
Runsom Precision offers high-quality CNC machining services for metal rivets, bolts, nuts, and screws. Additionally, we supply top-notch custom precision CNC machining solutions for prototyping and production processes. Our skilled technicians possess the necessary expertise to ensure optimal outcomes and quick turnaround times. Request an instant quote today!
Other Articles You May be Interested in:





