Chrome plating is widely used across industries such as manufacturing, production, and consumer goods due to its versatility. When applied to metal parts and products, it not only offers a protective coating but also imparts a glossy finish, enhancing their visual appeal. Chrome plating serves various roles whether for decorative purposes or to improve the functionality of machine components.
In situations where the previously resilient and attractive coating becomes damaged and unsightly due to wear and tear, or if there is a need to re-chrome a metal surface, it is required to eliminate this durable coating from the metal object. There are several options available for removing the chrome-plated layer, and the choice depends on the type of metal and the extent of chrome that needs to be removed.
To understand chrome plating better, we will explore what is chrome plating, how it works, the difference between its two types – hard chrome plating and decorative chrome plating, and methods to remove chrome plating in different ways.

What is Chrome Plating?
Firstly, let’s briefly discuss the electroplating. This will help to understand chrome plating better. Electroplating involves the addition of a layer of metal onto another type of metal. One of the main purposes of electroplating is to provide protection against corrosion. This is achieved by using a less corrosive or noncorrosive metal to cover a metal that is more susceptible to corrosion. Additionally, electroplating is used to enhance the lifespan of a product and to improve the aesthetics of metal surfaces.
Now, let’s return to the main question – what is chrome plating? Chrome plating, also known as chromium plating, is a specific electroplating technique that involves applying a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. The resulting product of chrome plating is called chrome.
Chrome is a silvery-white metal with a slight blue hue. When exposed to air, it readily forms a thin film on its surface, a process known as passivation. The layer of chrome plating offers multiple benefits, including corrosion resistance, increased surface hardness, easier cleaning, and improved aesthetics. In addition, the chrome plating layer exhibits high hardness, excellent heat resistance, and remarkable wear resistance.
While there are various compounds capable of producing glossy finishes, such as polished aluminum, chrome plating typically results in a brighter and more reflective surface. This characteristic gives chrome-plated objects a mirror-like quality, leading to more precise and accurate reflections.

Types of Chrome Plating
There are two types of chrome plating, namely hard chrome plating and decorative chrome plating. The specific type of chrome plating utilized is determined by its intended purpose and requirements.
Hard Chrome Plating
Hard chrome plating, which is also referred to as industrial or engineered chrome plating, involves applying a thick layer of chromium to engineering parts primarily made of steel. The standard thickness for hard chrome plating ranges between 0.02 to 0.04 mm, which is considerably thicker than decorative plating and is used for materials that require enhanced functionality and strength. This type of plating serves several purposes, including:
- Extend the lifespan of parts
- Provide excellent corrosion and wear resistance for valuable metal objects
- Reduce friction due to its exceptional lubricity and hardness
- Prevent parts from seizing and enhance their overall durability
- Increase chemical inertness, particularly in terms of oxidation resistance
Decorative Chrome Plating
Decorative chrome plating, also referred to as bright plating, is mainly aimed at enhancing the visual appeal of an object while also offering protection against corrosion and wear. The typical thickness range for decorative chrome plating is between 0.002-0.02 mm. Due to the thinness of the decorative chrome layer, its durability is not as robust as that of hard chrome plating.
It is worth noting that decorative chrome plating is sometimes called nickel-chrome plating because it is applied over a layer of nickel plating, rather than being directly applied to the metal substrate.
Decorative vs Hard Chrome Plating: Their Difference
Knowing the difference between hard and decorative chrome plating is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for your specific project. The following sections will outline the differences between these two types of plating in terms of thickness, properties, and applications.
1. Thickness
The primary difference between hard chrome and decorative chrome plating lies in the thickness of the applied chrome layer on the final product. Hard chrome plating is thicker than decorative chrome plating. Furthermore, an important aspect of decorative chrome plating is that it necessitates the presence of a bright nickel plate before the chrome plating is applied.
2. Property
Hard chrome plating imparts enhanced hardness and strength to materials, resulting in reduced friction, increased wear resistance, and long-lasting durability. In contrast, decorative chrome plating primarily focuses on enhancing the visual appeal of a component. While it does provide some level of wear resistance, it is not as pronounced as that achieved with hard chrome plating.
3. Applications
While both decorative chrome and hard chrome plating undergo the same manufacturing process, their applications differ significantly. Hard chrome plating is well-suited for industrial applications and situations involving high levels of stress. In contrast, decorative chrome plating is primarily utilized to achieve a desired appearance and provide a thin protective coating for various consumer products. In instances where the primary objective is aesthetic appeal, decorative chrome plating may sometimes employ inexpensive imitation chrome finishes instead of genuine chromium.
Methods to Remove Chrome Plating
Typically, chrome plating serves as a protective layer, offering corrosion resistance and increased durability to chrome-plated metals. However, over time, the chrome coating may become damaged due to wear and tear, similar to other surface treatments. This requires chrome plating removal from plastics or metals.
A variety of methods exist for removing or stripping the chrome plating layer from the substrate. Let’s have a look at each method in detail.
Specialized Equipment
Specialized machines are available for effectively removing chrome from different materials. One notable advantage of using these machines is their versatility, as they can be used for both plastics and metals. This is in contrast to chemical solutions, which often have limitations in terms of material compatibility.
1. Abrasive Blaster
Abrasive blasting, also referred to as sandblasting, is a technique that involves the use of tiny and fine pellets to abrade the chrome materials. The primary tool used for abrasive blasting is an abrasive blaster. These blasters are commonly found in auto shops, where they employ a high-pressure stream of abrasive particles to strip away the chrome coating, revealing the underlying metal surface without causing damage.
During the abrasive blasting process, it’s crucial to take necessary precautions and wear appropriate protective gear, such as goggles and masks. This is because the process can release very fine debris and dust into the air, which can be toxic and irritating if it comes into contact with the eyes and lungs.
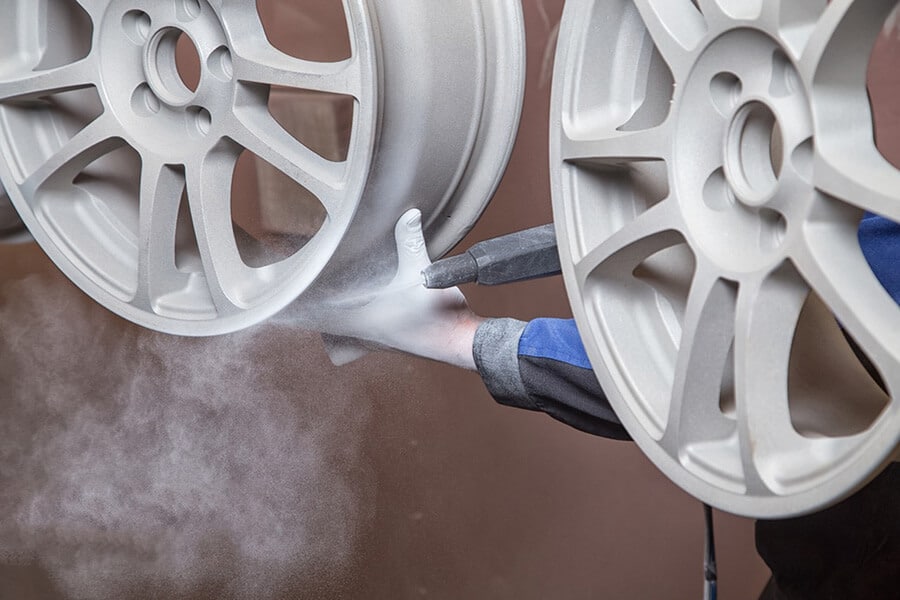

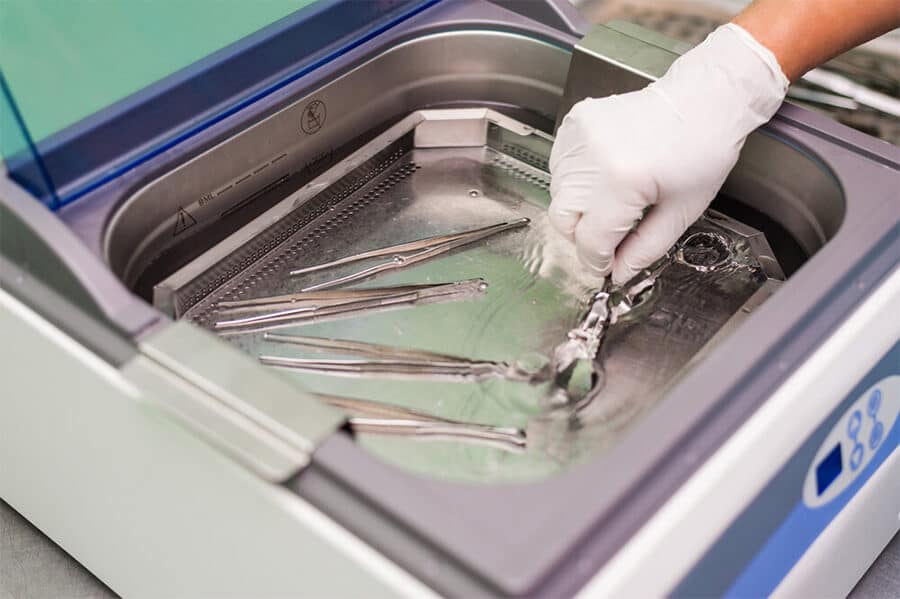
2. Ultrasonic Cleaner
Ultrasonic cleaners make the process of chrome removal simple and convenient. These cleaners utilize high-frequency sound waves to eliminate dirt, grime, and other deposits from surfaces. They are commonly employed for cleaning delicate electronic parts or jewelry.
In the case of chrome plating removal, ultrasonic cleaners operate by subjecting the chromium particles to high-frequency vibrations. This action causes the chromium to separate from the metal surface, resulting in the flaking off of the chrome layer. However, the limited size of ultrasonic cleaners only allows for the removal of chrome from relatively smaller materials.

Chemical Solutions
To initiate the process of chrome plating, chemical reactions are induced by an electric current. Conversely, chrome plating can be removed using specific chemical solutions. Chemical methods are a cost-effective approach for removing chrome plating compared to specialized machinery. However, it is crucial to exercise extreme caution when working with these chemicals due to their toxic nature. The use of appropriate protective gear, especially gloves, is essential.
1. Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, or muriatic acid, is a potent and corrosive acid. Its corrosive nature makes it effective for removing chrome from metal surfaces. Optimal results can be achieved by using a solution containing 30-40% concentration of hydrochloric acid to remove chromium.
Here is the process for removing chrome using hydrochloric acid:
- Prepare a 30% acid solution by mixing 1/3 part hydrochloric acid with 1 part water in a chemical-resistant container such as a heavy-duty plastic bucket. Alternatively, you can acquire a pre-mixed acid solution with the appropriate concentration.
- Submerge the chrome-plated object in the solution and allow the acid to work on removing the chrome.
- Once the chrome has been removed, take out the object from the container and thoroughly rinse it using soap and clean water.
- Leave the object to dry completely.
Chemical removal of chrome from plastic materials is not feasible due to the highly corrosive nature of many chemicals, especially at higher concentrations. These chemicals can cause significant damage to plastic materials.
2. Sodium Hydroxide
Just as hydrochloric acid is known for its acidic properties, sodium hydroxide is renowned for its alkaline nature. Sodium hydroxide solution is highly basic and can be effectively utilized for removing chrome plating from specific metals.
The process of removal is similar to using acid solutions – the chrome-plated materials are immersed in the sodium hydroxide solution and allowed to take effect. As a result, the chrome coating is stripped off the immersed materials. Then, cleanse the material with soap and water, thoroughly rinse it, and allow it to dry.
It is crucial to emphasize that if the base metal being dealt with is aluminum and the sodium hydroxide is mixed with water to form a solution, it can release hydrogen gas. This gas is highly explosive and must be avoided at all costs.
Reverse Electroplating
Reverse electroplating involves sulphuric acid, chromic acid, and a direct current. This process can be hazardous due to the production of toxic and carcinogenic chemicals. Moreover, the presence of a live current poses a significant risk of electrocution. Therefore, it is recommended that only professionals undertake this method.
In reverse electroplating, a mixture of acid and water is commonly used, typically in a ratio of 100 to 1. The final acid solution is obtained by combining chromic acid and sulphuric acid. This process is carried out within a temperature range of 120 to 150F. After achieving the optimal temperature, a DC power source is employed to expose the material to a negative charge. The fundamental principle behind this process is the removal of positive ions of chrome from the material.
Typical Process for Chrome Plating
There are two common processes for chrome plating: hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium.
Hexavalent Chromium
Hexavalent chromium plating is a traditional method of chrome plating primarily employed for functional applications. It’s important to note that hexavalent chromium, which is the predominant form used in this process, is considered highly toxic and a known human carcinogen.
Trivalent Chromium
Trivalent chromium plating predominantly employs chromium sulfate or chromium chloride as its primary component. In certain applications and thickness levels, trivalent chromium plating can serve as a substitute for hexavalent chromium plating. Notably, trivalent chromium is an environmentally friendly alternative to its hexavalent counterpart due to its significantly less toxicity.
How Does Chrome Plating Work?
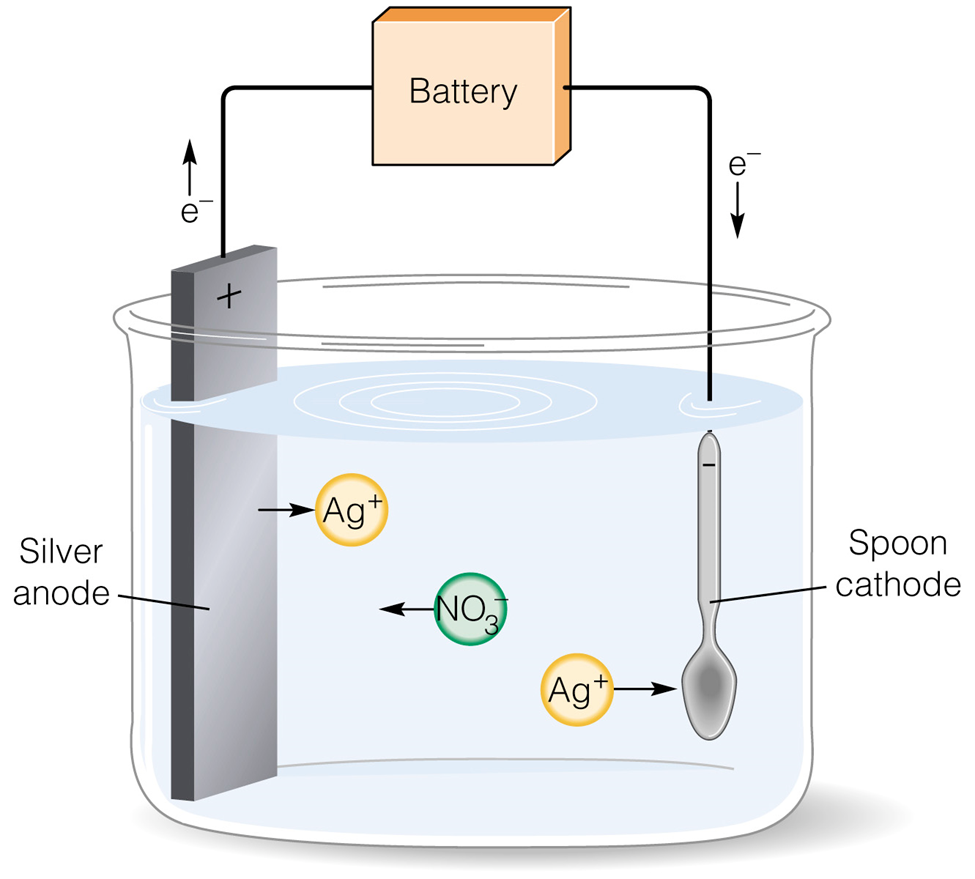
Chrome plating, as mentioned before, belongs to the category of electroplating processes, wherein a layer of metal is electrically deposited onto a metal surface. Given its electroplating nature, chrome plating necessitates the use of an electrical charge.
In this process, the manufacturer applies an electrical charge to a container containing chromium anhydride. The container itself is subjected to an electrical charge, initiating a chemical reaction that causes the chromium to adhere to the workpiece or object. In certain instances, additional steps such as finishing and polishing might be required. Absolutely, this description simplifies the actual complexity of the chrome plating procedures.
Application of Chrome Plating
The applications of chrome coating differ based on the specific material and purpose for which the chrome plating is required. When used for decorative purposes, chrome plating adds a smooth and glossy finish to the product, enhancing its visual appeal. In engineering applications, chrome plating can significantly increase the hardness of a metal surface. This heightened hardness improves resistance to wear, prevents galling, and enhances corrosion resistance.
- Hard chrome plating confers benefits to a wide range of machine components or parts. It is suitable for various base metals as it strengthens equipment components while preserving their original properties. Hard chrome plating is particularly well-suited for engineering parts that endure rigorous use over extended periods, such as shock absorbers, where strength and durability are crucial. The thickness of hard chrome plating can vary considerably based on the specific requirements of the project to ensure optimal performance.
- Decorative chrome plating is primarily sought after for its smooth and shiny appearance that is easy to clean. It has more limited application areas than hard chrome plating. Nevertheless, decorative chrome plating can still provide a thin protective coating on automobile parts, tools, and utensils, despite the lack of the same level of strength and durability as hard chrome plating.
Advantages of Chrome Plating
Chrome plating stands out as a prominent choice when it comes to metal plating. It offers a range of unique benefits that make it an ideal option for various applications.
Outlined below are eight compelling reasons why chrome plating should be your top choice when seeking to enhance your items through metal plating.
1. Prevention of Corrosion
The presence of corrosion poses a significant challenge for metal items as it can deteriorate their structural integrity and lead to their eventual destruction. Thankfully, chrome plating has the ability to inhibit the development of corrosion on materials.
Due to its corrosion-resistant properties, chrome plating is widely utilized in applications such as auto body parts that are particularly susceptible to rust. In fact, the automotive industry is the largest consumer of chrome due to its remarkable anti-corrosion capabilities.

2. Resilience Against Harsh Weather Conditions
Chrome plating strengthens materials by providing them with resistance against damage caused by severe weather conditions. Objects that have been chrome-plated are not easily affected by extremely high or low temperatures. They are also protected from harm caused by high or low levels of humidity.
Due to its capacity to withstand harsh weather conditions, chrome plating proves to be an optimal choice for reinforcing items that are constantly exposed to outdoor environments characterized by extreme climates.
3. Renewal to Brand New State
Chrome plating involves applying a coating that completely restores the appearance of an item. Through the process of chrome plating, items undergo a transformation to a brand-new state, eliminating any prior physical imperfections.
Chrome plating serves as a cost-effective solution for revitalizing old items, and restoring them to a like-new condition.
4. Appealing Aesthetics
Chrome plating is frequently selected for its ability to enhance the visual appeal of products and parts, giving them a smooth and shiny appearance. Through the relatively simple process of chrome plating, items undergo a transformation, acquiring a new look, texture, and surface quality.
The finish achieved through chrome plating is vibrant and attractive. The appealing aesthetics of chrome plating make it a favored option for items intended to be prominently displayed and serve a decorative purpose.
5. Non-damaging Impact on Substrate Material
Chrome plating is unique in its non-damaging effect on the substrate material. The application of chrome plating can be carried out at lower temperatures, ensuring that the underlying material remains undamaged.
In contrast, when metal plating is conducted at higher temperatures, it often leads to the deterioration and weakening of the substrate material.
6. Dealing with Intricate Shapes
When it comes to coating objects with unconventional and irregular forms, metal plating processes often face limitations. However, chrome plating stands out by its ability to be applied to irregularly shaped items, including objects that have bores or holes in their designs. This versatility makes chrome plating an excellent choice for various complex forms.
7. Adherence Strength
Unlike some other types of metal plating, chrome plating exhibits exceptional adherence to the substrate material. This strong bond between the chrome plating and the surface contributes to the durability of the items that undergo chrome plating.
The exceptional adherence of chrome plating significantly reduces the likelihood of flaking or de-lamination once it has been applied. This robust adhesion not only extends the lifespan of chrome-plated objects but also minimizes the need for subsequent repairs or maintenance over time.
8. Enhanced Lubricity
Among the various metal plating options available, chrome plating boasts exceptional lubricity. The lubricating properties of chrome plating offer numerous advantages that significantly contribute to its engineering value.
Lubricity plays a vital role in reducing friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and tear, and enhancing the longevity of chrome-plated items. Moreover, the lubricity of chrome plating helps to mitigate the occurrence of galling.

FAQs
Conclusion
The chromed layer serves multiple purposes such as corrosion resistance, improved surface hardness, easier cleaning, and enhanced appearance. Therefore, chrome plating is suitable for a wide range of commercial and industrial applications.
This article is a guide to chrome plating, covering its definition, the process involved, the differences between two types – decorative chrome plating and hard chrome plating, techniques for removing the durable chrome plated coating, and more.
Custom Chrome Plating – Runsom Precision Can Help

Executing the chrome plating process and removing chrome plating can be challenging due to the utilization of highly toxic chemicals. Consequently, it’s advisable to rely on professionals to ensure safety and achieve optimal outcomes.
Let Runsom Precision be your reliable manufacturing partner for top-notch electroplating services, including chrome plating. Our team of specialists has extensive expertise and utilizes advanced tools to maintain quality control over your final product and fulfill your requirements. Require an instant quote to start your projects or consult our experts on your surface finishing needs.
Other Articles You May Be Interested in: