Nickel plating is the electrolytic deposit of nickel coating onto a substrate. Nickel plating is a one-of-a-kind mix that works for both wear and corrosion resistance. It is also used for hardness, lubricity, and magnetic purposes. Other than that, it can enhance radiance, luster, and appeal. It also has good adhesive characteristics for successive coating layers, so nickel is frequently used as an ‘undercoat’ for other coatings like chromium and aluminum.
It is typically smooth and drab grey in appearance when used in engineering operations. Nickel works as a diffusion barrier for other metals like gold and silver, preventing substrate migration to the top layer. Along the same lines, in this article, we will discuss the types of nickel plating in various industrial processes, along with its applications – continue reading to learn more.
A Brief Explanation of Nickel Plating
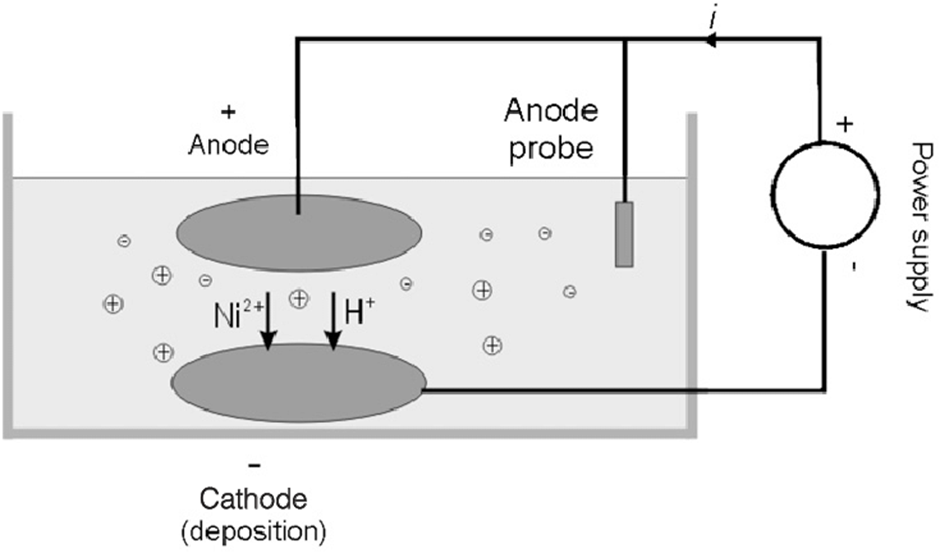
The procedure of coating nickel on a metal object is known as nickel plating. It may refer to electroplating with nickel or electroless nickel plating. The method of electroplating a thin layer of nickel onto a metal item is known as nickel electroplating. In comparison, electroless nickel plating is an auto-catalytic process that deposits a nickel coating on a substrate.
Unlike electroplating, no electric current is needed to travel through the solution to generate a deposit. Electroless nickel plating offers benefits over electroplating. The method remains free of flux-density and power supply concerns, gives an even deposit independent of workpiece shape, and may deposit on non-conductive surfaces with the correct pre-plate catalyst.
Nickel coating can be applied to all widely used metals and alloys. Substrates include copper and copper alloys, plastics, zinc and aluminum alloys, brass, and, lastly, unalloyed and low alloyed steel. Before nickel plating, the substrate must be free of any oil, scale, oxide, or grease. Apart from that, specific substrates such as zinc, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and plastics need to undergo specialized pre-treatments before the nickel plating procedure.
Types of Nickel Plating
Here we discuss the most widely used types of nickel plating:
Nickel Electroplating
Electroplating is a process that involves the application of a thin coating of metal or metal alloy to alter the physical or technical aspects of the surface of the object being plated. These properties may include electrical conductivity, appearance, durability, and performance.
Nickel electroplating technique has advanced significantly in the past fifty years, considering the efficient production of a broad scope of industrial coatings for functional and decorative applications. Electroplated nickel has commercial significance, with up to 150,000 tons deposited globally every passing year. This extensive application demonstrates this metal’s advantageous qualities and adaptability as a coating material. The ability to tailor the properties and appearance of nickel to individual purposes is a unique aspect of electroplating, accomplished by altering the composition of the electrolyte and the operating parameters.
Electroplated nickel has widespread applications. It is generally used to improve the usability, value, and aesthetic appeal of finished products such as consumer goods. Not only has that, but nickel coatings enhance the physical characteristics of various parts and components, such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. Many critical applications of nickel electroplating serve two purposes. These incorporate delivering better corrosion resistance and other functional properties and providing a bright, appealing finish.
The growing application of durable nickel-chromium coatings on plastics and aluminum components has been one of the most remarkable and recent breakthroughs in nickel plating. Bright, satin, black, and pearl coatings are famous for motorcycle, automotive, and commercial vehicle components, along with taps or faucets and bathroom fittings, metal furniture, door and cabinet fixtures, appliances, and consumer electronics.
Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless nickel plating involves coating nickel on a surface by a regulated chemical process or reduction, not dependent on an applied current. Hence, even when applying the coating to items with complicated shapes, it remains remarkably consistent and uniform. Hard disc drives are a common application for computers. Yet, other examples are metalizing plastics for electroplating, automobile brake cylinders, valves, pumps, and various engineering products.
Electroless nickel plating relates both wear and corrosion resistance with exceptional adhesion to all metals. Besides, this technique includes low-weight metals such as aluminum, which is becoming popular in the aerospace and automotive industries due to being lightweight.
These coatings are the top choice for preventing corrosion of essential materials and elements in severe environments. For example, these include the materials in automobile fuel systems, gearbox parts, turbochargers, and braking systems. It is used in aviation to coat electrohydraulic servo valves, engine mounts, compressor blades, landing gear, and other critical components.
Electroforming
Electroforming alludes to a necessary industrial process that employs nickel sulphonate and nickel chloride. Essentially, it’s an additive manufacturing technique that involves electrodepositing nickel onto a preformed mold or pattern called a mandrel. Subsequently, the mandrel is eliminated, leaving a nickel product that perfectly matches the texture and shape of the original substrate. Its different applications involve stampers for DVDs and holograms, CDs, rotary textile printing screens, radar waveguides, nickel foams for batteries, postage stamps & official documents, security printing for banknotes, etc.
Applications of Nickel Plating
In this section, we will discuss the several applications of nickel plating in various industries:
Nickel Plating In Coinage
Nickel plating used in coinage delivers glossy, attractive, and long-lasting “silver-colored” currency. Silver coinage usually refers to nickel-plated steel to convey its worth to the citizens via its bright and polished appearance. Governments and mints enjoy the low cost of nickel surfaces taking dye impressions for fine clarity and detail that will undoubtedly last for decades. Meanwhile, manufacturers and operators of vending machines rely on the magnetic signature of the nickel to authenticate the coin currency and allow only legal transactions. When the coins complete their lifespan, the nickel and steel come back and are recycled and reused.
Nickel Plating In the Automotive Industry
Nickel plating is widely employed in the automotive industry, where plating and coating are a considerable part of their processes. The innovation in the coating in the auto sector is constantly growing, and nickel is becoming essential for safety and durability. Coating nickel on plastic and aluminum parts delivers substantial cosmetic and longevity benefits. Zinc-nickel plating is exceptional in preventing corrosion, such as against salt spray, and is in a tremendous demand for automotive fasteners, bolts, and other components. It is employed in hydraulic systems, shafts in various engine elements, parking brakes, and automatic transmissions.
High-Performance Coating – Auto Industry
We have already established that the automotive industry has a high demand for nickel; now, let’s dive into why nickel is their preferred coating. The industry is quite picky, especially when choosing the suitable coatings to provide the best corrosion and wear resistance. Zinc-nickel plating is utilized for applications requiring significant corrosion and heat resistance with the most negligible deposit thickness. Therefore, it is the preferred material in the automotive sector for high-performance coatings of fasteners, bolts, and brake components. A zinc-nickel layer typically comprises 12-15% nickel, which may also be used on aluminum and magnesium substrates, becoming increasingly important in the automotive industry.
Nickel Plating For Plastics
Nickel coating on acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic moldings delivers exceptional durability for multiple applications. These encompass automotive, retail goods, builders’ hardware supplies, taps, electronic equipment, and more applications requiring glossy finishes.
Nickel Plating In the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector has the most stringent technical standards for safety and dependability features. The industry adheres to tight standards for all materials, coatings involved in the item development, and maintenance processes for aviation components, which are subjected to extensive testing and validation before their use. Nickel-based plating is vital in aerospace applications due to its unique functional qualities, including high adhesion, hardness, corrosion protection, wear and erosion resistance, and consistent layer thickness, even for intricate components. As a result, nickel, electroless nickel, and zinc-nickel coatings are becoming more popular in the aerospace sector for safety and performance.
Onsite Aircraft Maintenance
Onsite aircraft maintenance involves nickel brush plating, a specialized procedure for electroplating machine components onsite. This procedure can be applied with mobile devices brought to the aircraft site, rather than removing and hauling the parts to an industrial plating facility. It can result in considerable cost savings in aircraft maintenance. The technology is widely used in aerospace, especially for landing gear maintenance.
Nickel Plating In Electronics
Nickel plating is commonly used in electronic parts and components. With the ever-increasing demand for electronics throughout the globe, it has become equally important to perform nickel plating on electronic components to ensure safety and durability. It is similarly crucial in safety-critical applications where reliability is vital, and failure would have disastrous effects such as automobiles, trains, aircraft, and the energy sector. It is extensively used in electronic connectors, microprocessors, contacts, and integrated circuits (ICs) to ensure functionality and reliability. Because the criteria for such components are stringent, nickel plating is critical in the electronics sector, resisting corrosion, having good solderability, forming a barrier layer to prevent metal migration, and aiding in the prevention of ‘whiskers’ cause short circuits.

