To convey liquid, gas, steam, and hydraulic fluid, threaded pipes offer reliable sealing. Various materials can be used to produce these threads using techniques like CNC machining. One frequently encountered type of standard thread is the National Pipe Thread Taper (NPT) thread.
Here, we will cover the meaning of NPT, different NPT thread types, the fundamentals of NPT thread sizes, and the difference between NPT, NPS, & NPTE. You can also refer to the NPT thread size chart.
National Standard Taper Pipe Thread (NPT)
Thread Size Chart
| Nominal pipe size | Thread density | Thread pitch P | Hand-tight engagement | Effective thread | Overall length L4 | Actual outside diameter D | Tap drill | |||||||
| Length L1 | Turns | Diameter E1 | Length L2 | Turns | Diameter E2 | |||||||||
| inch | TPI | inch | mm | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | inch | mm | inch | mm | ||
| 1⁄16 | 27 | 0.03703704 | 0.9407 | 0.1600 | 4.32 | 0.28118 | 0.2611 | 7.05 | 0.2875 | 0.3896 | 0.313 | 7.950 | ||
| 1⁄8 | 27 | 0.03703704 | 0.9407 | 0.1615 | 4.36 | 0.37360 | 0.2639 | 7.13 | 0.38000 | 0.3924 | 0.405 | 10.287 | 0.339 | 8.6106 |
| 1⁄4 | 18 | 0.05555555 | 1.4111 | 0.2278 | 4.10 | 0.49163 | 0.4018 | 7.23 | 0.50250 | 0.5946 | 0.540 | 13.716 | 7⁄16 | 11.113 |
| 3⁄8 | 18 | 0.05555555 | 1.4111 | 0.2400 | 4.32 | 0.62701 | 0.4078 | 7.34 | 0.63750 | 0.6006 | 0.675 | 17.145 | 37⁄64 | 14.684 |
| 1⁄2 | 14 | 0.07142857 | 1.8143 | 0.3200 | 4.48 | 0.77843 | 0.5337 | 7.47 | 0.79178 | 0.7815 | 0.840 | 21.3360 | 23⁄32 | 18.2563 |
| 3⁄4 | 14 | 0.07142857 | 1.8143 | 0.3390 | 4.75 | 0.98887 | 0.5457 | 7.64 | 1.00178 | 0.7935 | 1.050 | 26.6700 | 59⁄64 | 23.4156 |
| 1 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4000 | 4.60 | 1.23863 | 0.6828 | 7.85 | 1.25631 | 0.9845 | 1.315 | 33.4010 | 1+5⁄32 | 29.3688 |
| 1+1⁄4 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4200 | 4.83 | 1.58338 | 0.7068 | 8.13 | 1.60131 | 1.0085 | 1.660 | 42.1640 | 1+1⁄2 | 38.1000 |
| 1+1⁄2 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4200 | 4.83 | 1.82234 | 0.7235 | 8.32 | 1.84131 | 1.0252 | 1.900 | 48.2600 | 1+47⁄64 | 44.0531 |
| 2 | 11+1⁄2 | 0.08695652 | 2.2087 | 0.4360 | 5.01 | 2.29627 | 0.7565 | 8.70 | 2.31630 | 1.0582 | 2.375 | 60.3250 | 2+7⁄32 | 56.3563 |
| 2+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.6820 | 5.46 | 2.76216 | 1.1375 | 9.10 | 2.79063 | 1.5712 | 2.875 | 73.0250 | 2+5⁄8 | 66.6750 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.7660 | 6.13 | 3.38850 | 1.2000 | 9.60 | 3.41563 | 1.6337 | 3.500 | 88.9000 | 3+1⁄4 | 82.5500 |
| 3+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.8210 | 6.57 | 3.88881 | 1.2500 | 10.00 | 3.91563 | 1.6837 | 4.000 | 101.6000 | 3+3⁄4 | 95.2500 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.8440 | 6.75 | 4.38713 | 1.3000 | 10.40 | 4.41563 | 1.7337 | 4.500 | 114.3000 | 4+1⁄4 | 107.9500 |
| 4+1⁄2 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 5.000 | 127.0000 | 4+3⁄4 | 120.6500 | |||||||
| 5 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.9370 | 7.50 | 5.44929 | 1.4063 | 11.25 | 5.47863 | 1.8400 | 5.563 | 141.3002 | 5+9⁄32 | 134.1438 |
| 6 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 0.9580 | 7.66 | 6.50597 | 1.5125 | 12.10 | 6.54063 | 1.9462 | 6.625 | 168.2750 | 6+11⁄32 | 161.1313 |
| 8 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.0630 | 8.50 | 8.50003 | 1.7125 | 13.70 | 8.54063 | 2.1462 | 8.625 | 219.0750 | ||
| 10 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.2100 | 9.68 | 10.62094 | 1.9250 | 15.40 | 10.66563 | 2.3587 | 10.750 | 273.0500 | ||
| 12 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.3600 | 10.88 | 12.61781 | 2.1250 | 17.00 | 12.66563 | 2.5587 | 12.750 | 323.8500 | ||
| 14 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.5620 | 12.50 | 13.87263 | 2.2500 | 18.00 | 13.91563 | 2.6837 | 14.000 | 355.6000 | ||
| 16 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 1.8120 | 14.50 | 15.87575 | 2.4500 | 19.60 | 15.91563 | 2.8837 | 16.000 | 406.4000 | ||
| 18 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.0000 | 16.00 | 17.87500 | 2.6500 | 21.20 | 17.91563 | 3.0837 | 18.000 | 457.2000 | ||
| 20 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.1250 | 17.00 | 19.87031 | 2.8500 | 22.80 | 19.91563 | 3.2837 | 20.000 | 508.0000 | ||
| 24 | 8 | 0.12500000 | 3.1750 | 2.3750 | 19.00 | 23.86094 | 3.2500 | 26.00 | 23.91563 | 3.6837 | 24.000 | 609.6000 | ||
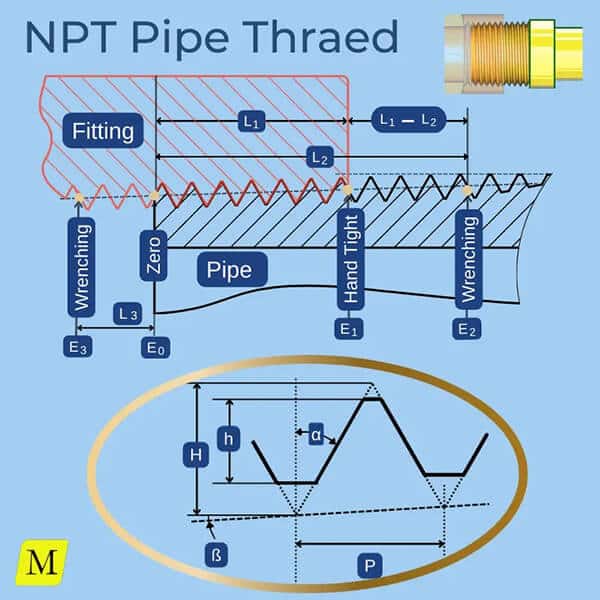
What Are NPT threads?
NPT (National Pipe Thread) is a set of global standards governing threads used for connecting hoses and fittings. These standards involve joining an external (male) thread with an internal (female) thread. While NPT threads serve a similar purpose as BSP threads, they are not usually interchangeable. NPT threads are further classified into tapered and straight thread series, each serving specific purposes such as providing rigidity, pressure-tight sealing, or both. The ANSI/ASME standard B1.20.1 defines the specifications for NPT threads.
NPT Threads possess the following defining traits:
- The angle formed between the taper and the center axis of the pipe is approximately 1.7899° or roughly 1°47′24″.
- The roots and crests of the threads are flat and truncated.
- The thread angle is 60°.
- The pitch is measured in threads per inch (TPI).
Pipe threads can be designed in different types to accommodate both threaded connections with and without thread sealants. For instance, the National Standard Taper Pipe Thread is specifically designed to create a seal when tightened. The larger diameter of the thread gradually compresses into a smaller diameter, resulting in the formation of a secure seal.
Common NPT Thread Types
Aside from NPT and NPS, there are various other types of American threading that are utilized for specific applications. These include NPSF, NPSC, NPTR, NPTF, NPSH, NPSM, NPSI, and NPSL.
Each of these thread types has its own distinctive characteristics and is designated with an abbreviation and a full name. This chart summarizes these types:
| Abbreviation | Full name | Shorter form | Features |
| NPT | American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread | National pipe taper | For creating seals, typically without any additional thread sealant; Available for connections in a wide range of applications |
| NPS | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread | National pipe straight | It requires using sealant to achieve a proper seal; For low-pressure sealing, male straight sometimes may be joined with female tapered |
| NPSI | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Intermediate Internal Straight Pipe Thread | National pipe straight–intermediate | Comparable to NPSF but slightly larger in size. For free-fitting mechanical joints in fixtures |
| NPSL | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Loose-fitting Mechanical Joints with Locknuts | National pipe straight–locknut | For use in conjunction with locknuts |
| NPSC | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Couplings | National pipe straight–coupling | For general couplings |
| NPSF | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Fuel Internal Straight Pipe Thread | National pipe straight–fuel and oil | For dry seal applications that involve soft materials |
| NPSH | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Hose Couplings | National pipe straight–hose | For use in water suction pipes and discharge hose couplings |
| NPSM | American National Standard Straight Pipe Thread for Free-fitting Mechanical Joints | National pipe straight–mechanical | For various rigid mechanical applications |
| NPTF | Dryseal USA (American) Standard Taper Pipe Thread | National pipe taper–fuel and oil | For dryseal connections in various services, particularly for fuel connections |
| NPTR | American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread for Railing Joints | National pipe taper–railing | For railings |
| PTF-SAE SHORT | Dryseal SAE Short Taper Pipe Thread | Pipe taper, fuel, SAE, short | Named after SAE International; Similar to NPTF but has one fewer turn |
Where the meaning of each letter is:
- N = National
- P = Pipe
- S = Straight
- C = Coupling
- R = Railings
- M = Mechanical
- L = Locknut
NPT threads can also be known as MPT (Male Pipe Thread) or NPT (M) when referring to external threads, and FPT (Female Pipe Thread) or NPT (F) when referring to internal threads. However, note that MPT and FPT are not specifically defined in the ANSI standard.
NPT Thread Sizes
- The most frequently used sizes for NPT threads are 1/8, 1/4, 3/8, 1/2, 3/4, 1, 1+1/4, 1+1/2, 2, 2+1/2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 inches. These sizes can be commonly found on pipes and fittings in the United States. Occasionally, smaller sizes below 1/8 inch and larger sizes exceeding 6 inches are utilized for specific purposes.
- In the NPT thread sizes chart, the pipe size does not indicate specific physical dimensions. Instead, it’s a trade size designation.
- To identify or determine a thread size, it’s important to consider both the threads-per-inch (TPI) and the outside diameter (OD) of the thread. This is because multiple sizes can have the same TPI. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the OD of a pipe or fitting and compare it to a thread size table for accurate identification.
- The taper rate of the threads is 1 inch for every 16 inches.
- An illustration of NPT thread designation: “1/8 – 27 NPT”.
- NPT and NPS threads cannot be used interchangeably. NPT threads have a tapered design, while NPS threads are straight. However, both NPT and NPS threads share the same thread angle, shape, and pitch.
The Difference between NPT, NPS, & NPTF
NPT vs. NPS
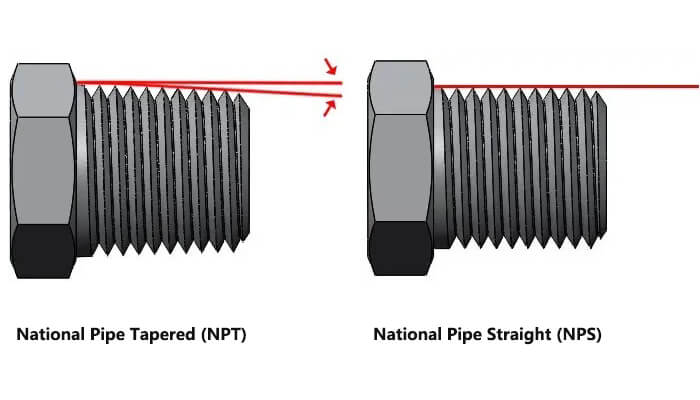
In the American National Pipe standard, two distinct categories exist: National Pipe Tapered (NPT) and National Pipe Straight (NPS). So what are the differences between these two?
NPT and NPS threads have identical thread angles, shapes, and pitch measurements (threads per inch). However, the NPT version features a tapered thread profile, visible when viewed from the side, while the NPS version does not have this taper. Both thread types have a 60° included angle and exhibit flat peaks and valleys. Tapered Pipe Thread is commonly used on pipe ends, nipples, and fittings such as couplings, elbows, and tees.
The sharply angled threads are important for ensuring tight joints without leakage. To achieve a proper seal, thread sealant or tape is typically required. On the other hand, Straight Pipe Threads necessitate the use of a gasket or O-ring to make a seal. While NPT and NPS threads can engage with each other, they do not seal properly when used together.
NPT vs. NPTF
The specifications for National Pipe Thread (NPT) are outlined in ANSI B1.20.1;
The specifications for National Pipe Thread Fuel (NPTF) are outlined in ANSI B1.20.3.
NPT and NPTF threads share the same number of threads per inch, pitch diameters, and taper-per-inch. However, they differ in terms of major and minor diameters, as well as the root and crest of the threads.
Although the NPTF thread crests fall within the parameters set for NPT, their range is smaller than that of NPT.
The NPTF thread roots are distinct from those of NPT. NPTF thread roots are intentionally designed to interfere with the crest of the mating thread in order to create a mechanical seal through thread form deformation during assembly. NPTF threads are categorized into two classes: Class 1 and Class 2. In contrast, NPT thread roots are designed to provide clearance with the mating thread crests upon assembly.
Conclusion
ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 defines the NPT thread as a standard thread type. This standard outlines the specific size, angle, and depth of the thread to maintain consistency in size and form. This consistency is crucial for establishing reliable and leak-free connections. This article has provided an overview of the NPT thread and offers a size chart for your reference.
Your CNC Machining Expert for Any Types of Threaded Parts – Runsom Precision
The Runsom Precision team, consisting of skilled engineers and machinists, possesses extensive knowledge of various thread standards and thread types. We’re well-versed in thread sizes, pitch sizes, and industry standards. With over ten years of experience in the CNC machining industry, we are dedicated to providing perfect solutions for customer projects. If you have any inquiries, please don’t hesitate to reach out or submit your 3D files online for an instant quote.
Other Articles You May Be Interested in:





