The laser CNC cutting machine, aka laser CNC engraving machine, being a high-precision CNC machine, is sure to soar with the advancements in technology. Increases in production capacity and workshop automation have resulted from the advent of laser CNC automation. Its one-of-a-kind design and method of operation make it ideal for cutting complicated shapes and tiny holes with pinpoint precision.
The fundamentals of computer numerical control (CNC) laser cutting will be covered in this article.
An Introduction to CNC Laser Cutter
CNC laser cutters, like other CNC machines, are guided through their cutting process by a set of computer instructions known as G-code. However, CNC laser cutters have a design that is a little bit different from that of typical CNC machines, and their technique of cutting works a little bit differently as well.
Cutting using a CNC laser cutter is a thermal technique that does not need physical touch. A focusing lens and nozzle are located in the laser head of a computer numerically controlled (CNC) laser cutter. This head and lens arrangement directs a laser beam through the nozzle on the workpiece, resulting in its melting and cutting into the required shape. Compressed gas (also running through the nozzle that releases the laser beam) is used in CNC lasers to temper the focusing lens and to discharge the vaporized metal from the workpiece.
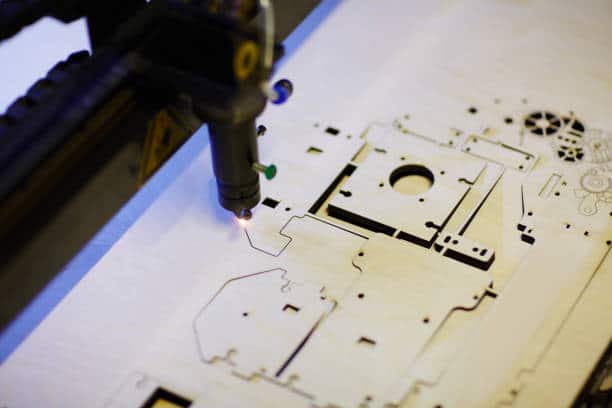
Let’s look at it from another angle. When a powerful laser beam is focused on a small area of metal, the heat density increases dramatically, causing the metal to heat up very quickly and vaporize, at least partially. Then, CNC technology directs the coordinated motions of the laser head and the laser beam over the work area to create the specified unique characteristics.
Types of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
The condition of the effective laser medium and the component of the effective laser medium are commonly used to classify different types of computer numerically controlled (CNC) laser cutters. Here are the three most popular kinds of lasers in use today:
CNC CO2 Laser Cutter
The CO2 laser cutter is a particular type of gas laser that uses carbon dioxide as the effective laser medium. Due to their high power output capabilities and great efficiency, they have become the most popular kind of laser cutter.
The power output of CO2 laser cutters may reach up to 15 kW, and their efficiency can reach up to 30 percent, which refers to the highest of all types of gas laser cutters. They are an excellent choice for cutting delicate features and sharp angles, in particular in sheet metals or metals having thicknesses of less than 10 millimeters. CO2 laser cutters with more cutting power are also capable of producing high cut accuracy on thicker metal substrates.
CNC Fiber Laser Cutter
Fiber laser cutters are a relatively new kind of laser technology in which the beam is generated by a series of diodes and focused by the use of a fiber-optic cable. When working with materials thinner than 5 mm, fiber laser cutters provide a quicker and smoother cutting than CO2 laser cutters.
While fiber lasers are functional with a wide variety of materials, particular care has to be taken with silver.
Machined parts made from silver are notoriously difficult to produce because the metal absorbs heat from the laser and begins to deform during cutting operations. Therefore, during fiber laser cutting processes, the best machine shops often utilize a bracket as a heat sink to dissipate the heat from the silver substrate.
CNC Crystal Laser Cutter
Beams for CNC crystal laser cutters are created from crystals such as neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (also known as Nd:YAG) and neodymium-doped yttrium ortho-vanadate (also known as Nd:YVO).
Unlike CO2 laser cutters, which are limited to thinner metals, crystal laser cutters have a greater intensity (or laser power) and can cut thicker metals. These cutters may be used on a wide variety of materials, from metals to glass to wood to plastics.
Materials Available for CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser machines are useful for cutting, engraving, marking, stippling, and etching a vast range of metal & nonmetal materials:
- Metal
Aluminum, titanium, brass, copper, silver, manganese, lead, chromium, stainless steel, carbon steel, tool steel, spring steel, etc. - Non-Metal
Acrylic, plastic, PMMA, polyester (PES), polyethylene (PE), polytetrafluoroethylenes (PTFE/Teflon), wood, textile, carbon fibers, etc.
Programming of Components on a CNC Laser Cutter
Files in 2D formats, like DXF or DWG, or 3D formats, like STEP or SAT, may be analyzed to provide insight into a design’s construction. Using this data, a flat shape is fabricated by adjusting the size of the cut to account for any necessary bend allowances or other factors that may impact the finished product. Software packages may determine the optimal component configuration for a particular sheet size.
Some common sheet sizes include 2 meters by 1 meter, 2.5 meters by 1.25 meters, and 1.5 meters by 3.0 meters. Likewise, scraps from completed projects are a useful source. We use a technique called CNC nesting to do this. By automating the nesting of many pieces inside a single sheet of metal or across multiple sheets of varying sizes, software like Radan® may maximize productivity. It is beneficial to arrange similar elements on the same sheet to maximize material use.
Compared to programming a punch press, CAM for laser cutting is often simpler. There are, however, numerous details to think about. The laser-cutting process requires many steps, including tag positioning (to keep the parts from toppling over in the nest), off-cutting (to keep the best-sized and shaped off-cut), and scrap-cutting (to break up the scraps into tiny pieces that will fall through the gaps in the laser cutter bed).
Pros and Cons of CNC Laser Cutting

Here are the advantages as well as disadvantages of the CNC laser cutting process.
Advantages
- Very little post-cutting work is required because of the narrow kerf, great accuracy, and acceptable kerf roughness.
- The laser substantially enhances the work atmosphere of the operator because of its high degree of automation, ability to be totally enclosed for processing, lack of pollution, and silent operation.
- It’s cheap to process. Ongoing and sizable processing will gradually lower the processing cost per component, although the initial investment in equipment is higher.
- The laser’s lack of contact means it can process quickly and efficiently with nothing in the way of resistance. Utilizing CAD/CAM software to program a CNC machine is not only a time and effort saver but also improves overall productivity.
- The laser’s high energy density is sufficient to melt any metal, so it works particularly well with materials that are challenging to work with because of their high brittleness, high hardness, and high melting temperature.
- Laser processing has the advantages of a high energy density, a fast action time, a limited heat-affected zone, little thermal deformation, and low thermal stress. Furthermore, the laser refers to a non-mechanical contact processing method. Therefore it places no mechanical stress on the substrate and may be used for high-precision operations.
- As a collection of computers that can be easily rearranged and customized, the CNC laser system is well suited for individualized processing, particularly for certain sheet metal components with complicated geometries and forms.
Disadvantages
- To produce thicker sheets (2.0mm and higher), it moves more slowly than punch presses.
- Costs for nitrogen or oxygen on heavier metal gauges are higher.
- Without making actual contact, the laser head cannot produce features such as dimples, knockouts, louvers, countersinks, or taps in a metal sheet.
- Lasers are ineffective when trying to cut perforated or mesh sheets.
Conclusion
CNC Laser Cutting is a great production tool for consumers because of its versatile cutting options and high precision in terms of measurements. But the fact that these technologies make machining easier in no way implies that CNC laser cutting is straightforward. If you care about the quality of your finished product, you should choose a reputable machine shop with a history of successfully producing components using CNC laser cutters.
Work with Runsom for Your CNC Machining Projects
Relying on our own system technology integration capabilities, focusing on technological commanding heights and the future development direction, and cooperating with reliable partners, Runsom can offer the best laser cutting process to accommodate the components being manufactured. And the quality and price always match each customer’s requirements and desires demanded.
Learn more about our CNC machining services.
Other Articles You May be Interested in: