Zinc commonly serves as a material for CNC machining due to its favorable characteristics and properties, ranging from corrosion resistance and electrochemical properties to ease of processing.
This article will offer a thorough examination of the qualities of zinc, various types of zinc alloys, and a wide range of applications. It also provides a detailed exploration of each aspect to ensure a comprehensive understanding of zinc machining.

Characteristics of Zinc
| Chemical Properties | As a chemically stable metal, zinc forms a dense oxide film when exposed to oxygen, effectively preventing further oxidation and exhibiting excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Physical Properties | Zinc exhibits good ductility and malleability, allowing it to be easily shaped into various forms and structures. |
| Electrical Properties | Zinc serves as a sacrificial protection material such as anti-corrosion coatings and battery manufacturing. |
Zinc Alloys Types for Machining


Zinc alloy is a material based on zinc, blended with other elements like aluminum, copper, magnesium, etc.
According to the different alloy elements and proportions, zinc alloys can be divided into various types, each with their specific physical and mechanical properties.
- Traditional Die Casting Zinc Alloys:
Including alloys like Zamak 2, Zamak 3, Zamak 4, Zamak 5, and Zamak 7. Zamak 3 is the most commonly used due to its good flowability and mechanical properties. - Aluminum Zinc Alloys:
Including ZA-8, ZA-12, ZA-27, etc. These alloys contain a higher proportion of aluminum, providing better dimensional stability and higher mechanical strength. - High-Temperature Zinc Alloys:
With high melting points and excellent heat resistance, these alloys are suitable for manufacturing parts, such as engine components, heat exchangers, and more. - ACuZinc Alloys Involving ACuZinc 5 and ACuZinc 10. These alloys are commonly utilized in the manufacture of mechanical components for automotive parts, aerospace components, electronic equipment, and various other industrial applications.
Processes in Machining Zinc Parts
When it comes to machining zinc parts, several common techniques can function to effectively manufacture and shape zinc components.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining plays a crucial role in the manufacturing process of zinc parts. Through precision cutting, it facilitates the manufacturing of zinc alloy parts with flexible and intricate geometries.

Milling
Milling involves removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutters. It is commonly used to create irregular and prismatic shapes or features on zinc parts.
Turning
Turning is a machining process that entails rotating a blank on a lathe while a cutting tool removes material. Additionally, it is effective for creating cylindrical shapes on zinc parts.
Drilling
Drilling is the operation of creating holes in zinc metal utilizing drill bits of various length-to-radius ratios equipped with helical flutes. Furthermore, it is essential for incorporating fasteners or other components into zinc assemblies.
Grinding
Grinding is a finishing process that uses abrasive particles to smooth the surface of zinc parts and achieve tight dimensional tolerances.

Die Casting
Die casting encompasses injecting molten zinc metal into a die cavity under high pressure. It is particularly suitable for zinc alloys with intricate shapes and tight tolerances.
Electro-Discharge Machining (EDM)
Unlike traditional machining processes, EDM is the operation utilizing electrical discharges to shape and form workpieces. In this context, Zinc metal’s exceptional electrical conductivity exemplifies its versatility in the field of machining.
Surface treatment of zinc alloys
There are several common options for surface treatment of zinc parts:
Electroplating
Zinc can combine with chromium, nickel, or other metals through plating, to enhance their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
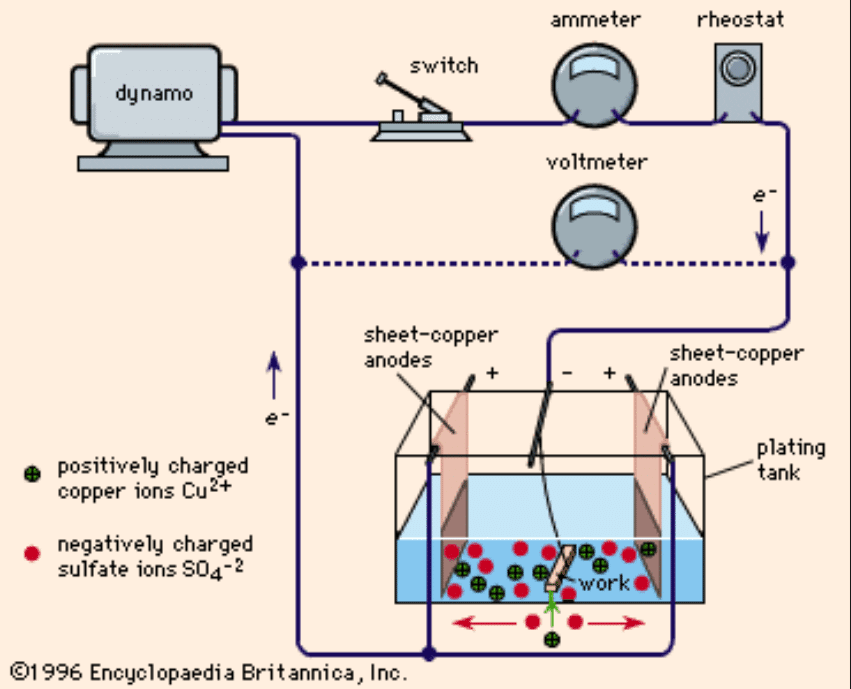
Mechanical Polishing
Polishing can elevate the surface finish and visual quality of zinc alloys, making it suitable for applications that prioritize top-notch decorative standards.
Creating a thin protective layer of oxides on the surface of zinc metal can enhance surface hardness and corrosion resistance.
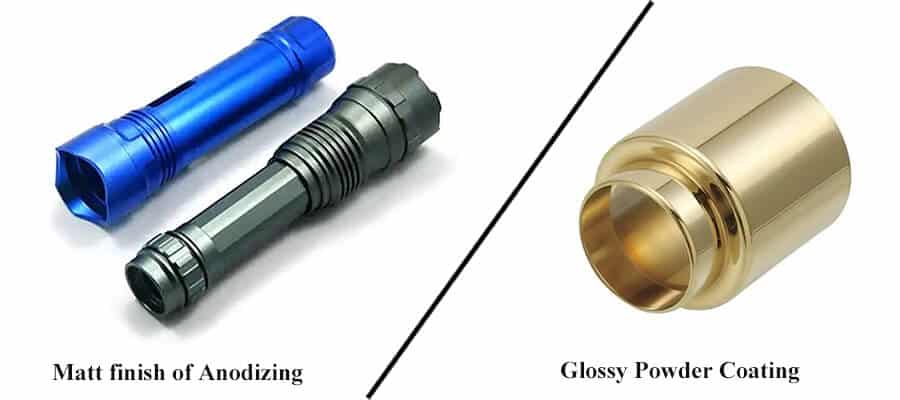

Powder Coating
It provides a protective layer that enhances the corrosion resistance of zinc alloys, offering a range of colors and decorative effects.
Chemical treatment:
Some chemical treatments, such as cleaning, pickling, and passivation, ensure zinc metal components meet quality standards.
Machinability of Zinc Metal
As a metallic material, zinc alloys possess distinct characteristics concerning their machining properties:
·Plasticity
Zinc exhibits commendable plasticity, rendering it suitable for various pressure processing methods such as die casting.
·Hot Workability
Their specific temperature range makes them ideal for hot extrusion, hot rolling, forging, and other related processes.
·Cutting Processing
Zinc alloy demonstrates relatively good machining performance, facilitating turning, drilling, milling, and a variety of other machining operations.
·Formability
Zinc boasts ease of shaping and can be used to fashion parts of diverse shapes through cold and hot forming techniques.
·Weldability
Zinc displays a certain degree of weldability, allowing it to compatibilize with common welding processes like as-shielded welding.
Key Techniques for Efficient Zinc Alloy Machining
During zinc alloy processing, it is crucial to consider material characteristics, process control, and efficient production. The following are key techniques to ensure the production of high-quality and efficient zinc alloy products:
·Comprehensive Understanding of Material Characteristics
In-depth understanding of the physical and chemical properties of zinc alloys to optimize processing techniques and ensure product quality and precision.
·Precision Control of Temperature and Pressure
Precise control of temperature and pressure is essential, as even minor variations can significantly impact product quality.
·Adopting Lean Production Principles
Optimizing processing workflows, reducing waste, and enhancing production efficiency and product quality.
·Utilization of Advanced Cooling Systems
Implementing efficient cooling systems to ensure process stability and product quality.
·Regular Maintenance and Cleaning of Equipment
Maintaining equipment in good condition, especially through regular cleaning and maintenance of metal mold processing equipment to ensure product surface quality.
Advantages of Zinc Alloy in Machining
Good Ductility and Malleability
It is easily shaped and formed into various structures as it is highly ductile and malleable.
Easy Machining
It is easy to process and fabricate with the low melting point.
Environmentally Friendly
Zinc alloy is a sustainable and recyclable material that facilitates protection of the environment.
Cost-effective
Zinc is generally less expensive than other metals, making it a cost-effective option for many applications.
Applications of Zinc Parts
As a versatile metal material, zinc finds broad application in various sectors:
| Construction Industry | Using zinc in the production of roofing, pipelines, and railings, among other construction materials. |
| Electronics Industry | It serves as a raw material for battery production and in the fabrication of casings for electronic devices. |
| Automobile Industry | Utilizing zinc alloy in automotive body panels, anti-corrosion coatings, and more. |
| Medical Devices | Employing zinc metal in the production of surgical instruments and medical materials. |
Future Development of Zinc Machining
As scientific and technological advancements continue, the field of zinc processing also experiences continuous innovative development:
| Sustainable Development | Driving the adoption of environmentally friendly processing technologies to reduce energy consumption and environmental pollution. |
| Material Applications | Exploring the application of zinc in 3D printing, advanced materials, and other domains to expand the scope of zinc’s applications. |
| Smart Manufacturing | Introducing smart manufacturing technologies to enhance the precision and efficiency of zinc processing. |
Protection Measures in Machining Zinc
Ensuring zinc processing safety is vital for operator well-being, environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and improved production efficiency. Below are pertinent protective measures:
·Ventilation
Ensure that the processing areas are equipped with robust ventilation systems to mitigate respiratory issues stemming from the accumulation of zinc dust. Timely removal and disposal of zinc dust generated during processing is essential.
·Respiratory Protection
Workers must use appropriate respiratory protective equipment, especially when dealing with molten zinc materials, to prevent inhalation of harmful gases and dust.
·Safe Operations
Comprehensive training for operators is crucial to instill the knowledge of safe operation of processing equipment, minimizing the risk of accidents.
·Fire and Explosion Protection
Due to the potential fire and explosion hazards while zinc is in a molten state, pertinent protective measures such as fire retardant coatings and explosion-proof equipment need to be implemented.
·Waste Disposal
Proper disposal measures should be in place for the waste generated from zinc processing to prevent environmental pollution.
·Personal Hygiene
Regular health check-ups for workers are imperative to ensure they are not adversely affected by prolonged exposure to zinc.
Conclusion
The processing of zinc spans a wide spectrum of domains, encompassing materials science, engineering technology, and innovative applications that go beyond conventional metalworking processes. Through ongoing research and development, it is believed that the field of zinc processing will witness further breakthroughs and development, injecting new vitality and opportunities into various industries.
FAQs
Choose Runsom Precision Machining Your Zinc Alloy
In Runsom Precision, you can rest assured that we are dedicated to meticulously crafting each stage of your project, from design to the finished product. Moreover, Runsom Precision’s meticulous service and professional engineering team can also ensure full communication with customers, making the process of customizing zinc alloy parts smooth and ultimately meeting customer expectations. Feel free to obtain an instant online quote at any time so that you can promptly understand the cost of the customized service.



