Welcome to our comprehensive analysis of the fusion between CNC technology and infrared thermal imaging. We aim to provide an in-depth understanding through an exploration of the machinery’s fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the crucial role played within various sectors. Together, we will unravel the multifaceted interplay between CNC technology and infrared thermography equipment, delving into its prevalent applications and future potential.
Basic Principles of Infrared Thermal Imaging
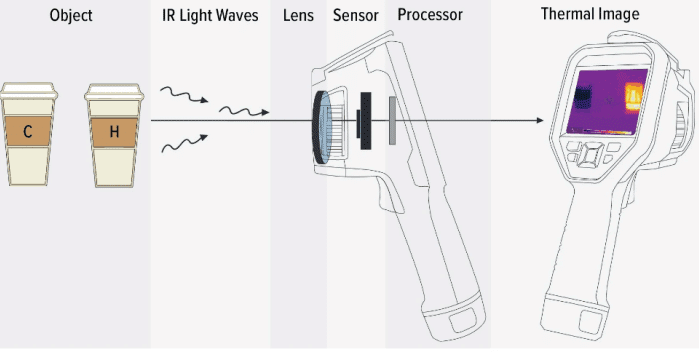
IR Thermal Imaging technology employs photoelectric methods to detect specific infrared band signals emitted by objects. These signals are then translated into distinguishable images and graphics with calculated temperature values. This process can be distilled into the following steps:
1. Receiving Infrared Radiation
The micro shovel array detector in the infrared thermography camera captures the infrared radiation, measuring the intensity in precise areas.
2. Optical System Reception
Utilizing lenses or mirrors, the built-in optical system focuses the received infrared radiation on the image plane, ultimately influencing image quality.
3. Signal Conversion
The infrared radiation, once measured, is converted into an electrical signal. Each detector unit then translates it into a corresponding voltage or current signal before transmitting it to the signal processing part.
4. Signal Processing and Image Generation
The received electrical signal undergoes amplification, filtering, and digitization within the signal processing section to generate the corresponding infrared thermal image. Each pixel’s brightness or color reflects the area’s temperature.
5. Display and Analysis
The generated infrared heat mapping is displayed on a screen for users to observe and analyze.
Navigating CNC Machining Technology
CNC machining technology revolves around the intricate control of machine tool movement through computer numerical control systems. Noteworthy for its high precision, efficiency, automation, and flexibility, it facilitates the precise processing of complex parts, thereby reducing production cycles and labor costs.
The Pivotal Role of CNC Technology in IR Thermal Imaging Equipment
| Manufacturing Accuracy | CNC technology is pivotal in ensuring the accuracy and stability of infrared thermography equipment components, such as lenses and mirrors, along with supporting mechanical structures. |
| Efficient Production | CNC technology facilitates the mass production of IR thermal imaging equipment by accelerating production and enhancing processing efficiency and consistency. |
| Complex Structure Processing | The technology adeptly processes complex optical and mechanical structures, ensuring the delivery of exceptional equipment performance. |
| Customized Manufacturing | The capability to customize IR thermal imaging equipment to meet varied customer needs is a testament to CNC technology’s adaptability. |
| Automated Production | Reducing human intervention, CNC technology improves production efficiency and product quality. |
Types of Infrared Thermal Imaging Equipment
1. Infrared Thermal Imaging Camera
Primarily used to obtain infrared thermal images of target surfaces from long distances, it detects temperature anomalies in electrical systems, thermal defects in building structures, and more.

2. IR Thermal Imaging Thermometer
Measures the temperature of the target surface and displays the temperature distribution through heat maps.

3. Infrared Thermal Imaging Drone
Integrating an infrared thermal imaging camera facilitates tasks such as aerial photography, inspections, and search and rescue operations.

IR Thermal Imaging Equipment for Military
1. Navigation and Targeting
Elevating target accuracy and fire strike precision, this equipment assists navigation systems in complex terrains for seamless military operations.
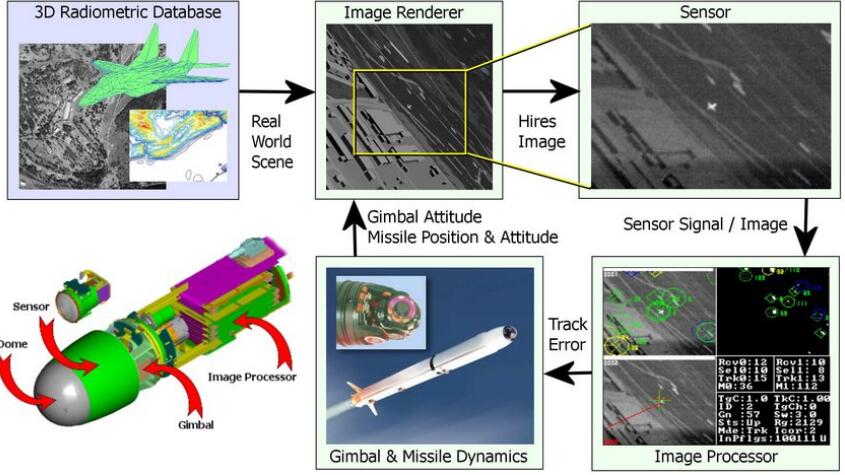
2. Missile Guidance
Incorporating IR imaging significantly boosts missile capabilities by extending detection ranges, improving identification, countering decoys, and augmenting missile potency.
3. Against Stealth Aircraft
Infrared thermography’s ability to capture heat radiation effectively counters stealth aircraft hideouts, offering a unique advantage in detection.
Infrared Thermography Technology for Smart City Construction

1. Fire Prevention
Early detection through temperature monitoring in crucial sectors such as power plants, petrochemical industries, and forests, ensures rapid alarm triggering and fire prevention.
2. Drone Inspection
The integration of IR thermal imaging with drones enhances disaster relief efforts, facilitates criminal apprehension, aids in power line inspections, supports scientific research, and improves efficiency in industrial and agricultural sectors.
3. Security Monitoring
Enabling 24-hour surveillance, infrared thermal imaging secures smart cities, irrespective of lighting conditions.
4. Smart Transportation
Aligning with intelligent transportation systems, IR thermal imaging optimizes road traffic management, offers real-time traffic insights, and supports emerging technologies like self-driving cars.
Thermal Imaging Cameras for Medical Imaging
1. Diabetic Foot Screening
Through thermal images, early signs of reduced or blocked blood supply in diabetic patients are detectable, aiding in proactive healthcare.
2. Tumor Diagnosis
Effective in detecting specific cases like breast cancer, providing critical diagnostic support for improved patient care.
3. Diagnosis of Cervical and Lumbar Spondylosis
Infrared thermal imaging supports the precise diagnosis of cervical and lumbar spine conditions, as evident in the comparative analysis of patients, enabling accurate localization of diseases.
4. Coronary Heart Disease Detection
Utilizing infrared imaging for temperature detection, potential heart conditions like coronary heart disease are diagnosed efficiently, offering valuable insights through temperature changes in the precardiothoracic area.
Custom Manufacturing Processes for Thermal Imaging Equipment
1. CNC Machining
Utilizing CNC machines, this process ensures high precision and efficiency through pre-programmed tool movement sequences.
2. Turning
Involves rotating the part while the tool cuts materials into the desired shape, commonly used for processing shaft parts.
3. Milling
Fixing the component on a machine table, and milling involves cutting the part surface in various directions, suitable for flat, curved, and complex contour parts.
4. Grinding
Precision machining is achieved by using abrasive tools to grind the part surface.
5. Die Casting
This process involves cutting, shaping, or punching metal sheets using dies on a punch machine, ideal for mass-producing simple parts.
The Future Development of IR Thermal Imaging Technology
The future trends in infrared thermal imaging technology include:
1. Expanded Application Fields
Anticipated integration in emerging sectors like automotive assisted driving, personal electronics, and the Internet of Things to drive advancements in drone technology and autonomous driving.
2. Technological Innovation
Continuous enhancement in performance and functionality through wafer-level packaging, multi-modal fusion imaging, and deep learning image processing technologies.
3. High Performance and Intelligence
Development aimed at high performance, precision, stability, intelligence, networking, and portability, ushering in a new era of advanced thermal imaging capabilities.
4. Market Expansion and Adaptation
Infrared thermal imaging’s future trajectory involves broader application scopes, increased innovation, global competitiveness, and a shift toward highly intelligent solutions.
Selecting an Infrared Thermal Imaging Equipment Manufacturer
When considering an infrared thermal imaging equipment manufacturer, pay attention to the following aspects:
| Product Quality | Prioritize manufacturers with a solid reputation; assess product certifications, performance, and user feedback. |
| Technical Proficiency | Opt for manufacturers at the forefront of technology for cutting-edge infrared thermal imaging solutions. |
| Customization Capabilities | If unique needs arise, choose manufacturers with a proven track record in customization and production expertise. |
| After-Sales Support | Evaluate the manufacturer’s after-sales services, including warranties, repair options, and technical assistance to ensure ongoing operational efficiency. |
Conclusion
After delving into this blog, you now possess a deeper understanding of CNC technology’s functioning and its pivotal role in IR thermal imaging equipment. Furthermore, you’ve gained a comprehensive insight into the multifaceted applications of infrared thermal imaging across various domains. The future of IR thermal imaging technology will usher in further expansion, introducing innovative applications in diverse fields.
If you are seeking superior-quality infrared thermography imaging equipment and services, consider Runsom Precision. Renowned for high-grade products, robust technical expertise, customization capabilities, exceptional after-sales support, and continuous innovation in both infrared thermal imaging and CNC technology, Runsom Precision is dedicated to providing diversified solutions. For any inquiries, refer to the FAQ section or promptly obtain a quote.


