In zinc machining, our focus extends beyond traditional metalworking processes to encompass an in-depth exploration of this pivotal material’s diverse processing techniques and varied applications. Additionally, zinc holds significance across a spectrum of applications within its processing domain, as it is widely employed in multiple industrial sectors.
This article will provide comprehensive insights into zinc properties, alloy classification, machining, future trends, and essential protection measures, offering a detailed exploration of each aspect for a holistic understanding of zinc machining.

Characteristics of Zinc
| Chemical Properties | Zinc, a chemically stable metal, forms a dense oxide film when exposed to oxygen, effectively preventing further oxidation and exhibiting excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Physical Properties | Zinc exhibits good ductility and malleability, allowing it to be easily shaped into various forms and structures. |
| Electrical Properties | Commonly using zinc as a sacrificial protection material and often employing it in anti-corrosion coatings and battery manufacturing. |
Zinc Alloys


Zinc alloy is a material based on zinc, alloyed by adding other elements (such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, etc.). According to the different alloy elements and proportions, zinc alloys can be divided into various types, each with its specific physical and mechanical properties.
- Traditional Die Casting Zinc Alloys:
Including alloys like 2, 3, 4, 5, and 7.
Zamak 3 (Zinc Alloy 3) is the most commonly used due to its good flowability and mechanical properties. - High Aluminum Zinc Alloys:
Including ZA-8, ZA-12, ZA-27, etc.
These alloys contain a higher proportion of aluminum, providing better dimensional stability and higher mechanical strength. - High-Temperature Zinc Alloys:
Have high melting points and heat resistance.
Suitable for manufacturing parts that need to withstand high-temperature environments, such as engine components, heat exchangers, and more.
Zinc Machining Techniques
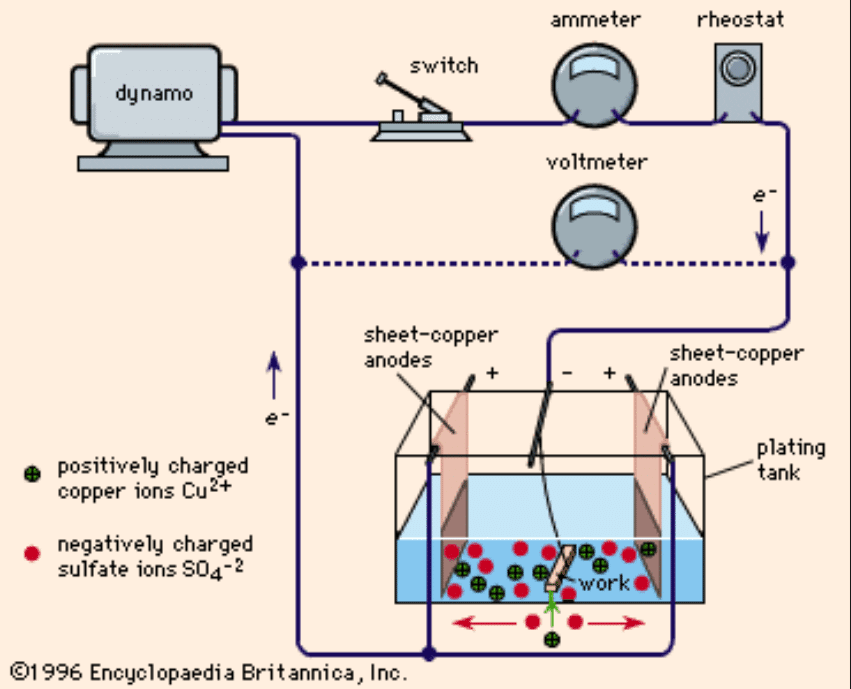
| Smelting and Casting | Melting zinc ore to produce pure zinc and cast it into various zinc alloy products. |
| Cold-Working and Hot-Working | Utilizing zinc’s plasticity and malleability, cold-working or hot-working processes in producing shapes such as zinc sheets and tubes. |
| Electroplating | Leveraging zinc for anti-corrosion treatment and aesthetic enhancement based on its electrochemical properties for electroplating |
Machinability of Zinc
As a metallic material, zinc possesses distinct characteristics concerning its machining properties, outlined below:
·Plasticity
Zinc exhibits commendable plasticity, rendering it suitable for various pressure processing methods such as die casting.
·Hot Workability
Zinc demonstrates favorable hot workability within specific temperature ranges, making it ideal for hot extrusion, hot rolling, forging, and other related processes.
·Cutting Processing
Zinc showcases relatively good cutting performance, making it conducive to turning, drilling, milling, and various other machining operations.
·Formability
Zinc boasts ease of shaping and can be used to fashion parts of diverse shapes through cold and hot forming techniques.
·Weldability
Zinc displays a certain degree of weldability, making it compatible with common welding processes like arc welding, gas-shielded welding, and more.
Zinc materials are receptive to surface treatments such as galvanizing and hot-dip galvanizing, effectively enhancing their anti-corrosion performance.
Key Techniques for Efficient Zinc Alloy Machining
During zinc alloy processing, it is crucial to consider material characteristics, process control, and efficient production. The following are key techniques to ensure the production of high-quality and efficient zinc alloy products:
·Comprehensive Understanding of Material Characteristics
In-depth understanding of the physical and chemical properties of zinc alloys to optimize processing techniques and ensure product quality and precision.
·Precision Control of Temperature and Pressure
Precise control of temperature and pressure is essential, as even minor variations can significantly impact product quality.
·Adopting Lean Production Principles
Optimizing processing workflows, reducing waste, and enhancing production efficiency and product quality.
·Utilization of Advanced Cooling Systems
Implementing efficient cooling systems to ensure process stability and product quality.
·Regular Maintenance and Cleaning of Equipment
Maintaining equipment in good condition, especially through regular cleaning and maintenance of metal mold processing equipment to ensure product surface quality.
Application Areas of Zinc
As a versatile metal material, zinc finds broad application in various sectors:
| Construction Industry | Using zinc in the production of roofing, pipelines, and railings, among other construction materials. |
| Electronics Industry | It serves as a raw material for battery production and in the fabrication of casings for electronic devices. |
| Automobile Industry | Utilizing zinc in automotive body panels, anti-corrosion coatings, and more. |
| Medical Devices | Employing zinc in the production of surgical instruments and medical materials. |
Extensive Application of CNC Technology in Zinc Alloy Machining
In the realm of zinc processing, CNC technology has brought about a revolutionary transformation in the processing of zinc alloy components. By enhancing precision control over dimensions and surface treatments, the CNC technique has become a key driving force in the processing of zinc alloy products. In fields such as electronics and electrical appliances, zinc alloy die-castings processed through CNC technology exhibit superior aesthetics and corrosion resistance, meeting the industry’s demand for high-quality products. The widespread application of customized zinc alloy CNC components in domains such as smart homes and sports equipment signals an industry shift towards the adoption of environmentally friendly and aesthetically pleasing zinc alloy products, presenting new development opportunities in the market.
Future Development of Zinc Machining
As scientific and technological advancements continue, the field of zinc processing also experiences continuous innovative development:
| Sustainable Development | Driving the adoption of environmentally friendly processing technologies to reduce energy consumption and environmental pollution. |
| Material Applications | Exploring the application of zinc in 3D printing, advanced materials, and other domains to expand the scope of zinc’s applications. |
| Smart Manufacturing | Introducing smart manufacturing technologies to enhance the precision and efficiency of zinc processing. |
Protection Measures During Zinc Machining
Ensuring zinc processing safety is vital for operator well-being, environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and improved production efficiency. Below are pertinent protective measures:
·Ventilation
Ensure that the processing areas are equipped with robust ventilation systems to mitigate respiratory issues stemming from the accumulation of zinc dust. Timely removal and disposal of zinc dust generated during processing is essential.
·Respiratory Protection
Workers must use appropriate respiratory protective equipment, especially when dealing with molten zinc materials, to prevent inhalation of harmful gases and dust.
·Skin Protection
Operators should wear suitable work attire and gloves to shield the skin from corrosion and irritation when in contact with processing fluids.
·Safe Operations
Comprehensive training for operators is crucial to instill the knowledge of safe operation of processing equipment, minimizing the risk of accidents.
·Fire and Explosion Protection
Due to the potential fire and explosion hazards while zinc is in a molten state, pertinent protective measures such as fire retardant coatings and explosion-proof equipment need to be implemented.
·Waste Disposal
Proper disposal measures should be in place for the waste generated from zinc processing to prevent environmental pollution.
·Personal Hygiene
Regular health check-ups for workers are imperative to ensure they are not adversely affected by prolonged exposure to zinc.
Conclusion
The processing of zinc spans a wide spectrum of domains, encompassing materials science, engineering technology, and innovative applications that go beyond conventional metalworking processes. Through ongoing research and development, it is believed that the field of zinc processing will witness further breakthroughs and development, injecting new vitality and opportunities into various industries.
FAQs
Choose Runsom Precision Machining for Your Zinc Alloy Needs
By choosing Runsom Precision as your comprehensive solution partner, you can rest assured that we are dedicated to meticulously crafting each stage of your project, from design to the finished product. Moreover, Our commitment to customer satisfaction remains unwavering, as we prioritize product quality through cost optimization and enhanced work efficiency. Visit our website for more information or to request an instant online quote and discover how as a leading rapid manufacturing company, we utilize state-of-the-art equipment and a highly skilled team to deliver zinc alloy components meeting stringent precision and tolerance standards.



