Injection Molding is a cost-effective manufacturing technology for identical plastic parts with high tolerance in mass-production. In injection molding process, polymer granules will be melted and injected into molds under pressure, liquid plastic will cool, solidify and final eject form molds. The materials applied in injection molding are thermoplastic polymers, which can be colored or filled with other additives. Most of plastic parts around your are manufactured by injection molding method, form electronic enclosures, to kitchen appliances and car parts.
Injection molding is widely applied in reason of its dramatic low cost in high volume production. It also provides high repeatability and good design flexibility. The main restriction of injection molding are economical issues, high initial investment of molds manufacturing is required, and long turn-around time from design to final production is at least 4 weeks.
Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is popular used for consumer products and engineering applications, almost every plastic products around you. The main reason is it can produce plastic parts at high volume with very low cost per unit. However, comparing to other manufacturing technologies, there is a high start-up cost of custom tooling, which is between$3,000 and $100,000 depending on complex structures, molds materials and accuracy.
Injection molding machines
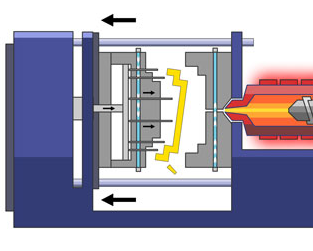
An injection molding machine is normally consist of 3 main parts: Injection Unit, Mold Unit and Ejector Unit. Each of these system has their basic operation mechanics and affect the final result in injection molding process.
Injection molding working process:
Polymer particles are dried and placed in the hopper, and mixed with color pigment or reinforce additives.
These particles are fed into the barrel, then heated, mixed and moved towards the molds by a pitch screw. The screw and barrel geometry are optimized to build up pressure and melt the materials.
Then the ram moves forwards and the melted plastic is injected into molds by the runner system. As the materials cool down, it solidifies and take mold shape.
Finally, the molds open and push out solid parts by ejector pins. The molds then close and repeat process.
This whole process is repeated fast, this cycle take almost 30 to 90 seconds depending on parts size. After ejection, it is dispensed on holding containers. Usually, injection molded parts can be used right way with little post-operations.
Injection Unit
Injection unit will melt raw plastics and guide it into molds, it consists of hopper, barrel and reciprocating screw.
The runner system
This is a channel to guide melted plastic into molds cavities. It will control the flow and pressure of liquid plastic and remove after ejection. Runner system usually consist of 3 sections: sprue, runner, gate.
Sprue is the main channel where all melted plastic flow into mold.
Runner connects sprue to the gates, it will spreads melted plastic into two halves of molds. There will be one or more runners to guide materials into multiple parts.
Gate is the entry point of melted materials into molds cavities. Its geometry and location is very important to determine plastic flows.
Different gate types are suitable for different applications, we have 4 typical gates in injection molding:
- Edge gate: this gate is the most common gate type, it can inject material at parting line of two halves. The runner system should be removed manually later, and left a small defect at injection point.
- Tunnel gate: this gate inject material below the parting line. The runner system will snap off once parts are ejected from molds, this gate is ideal for very large volume production.
- Post gate: this gate inject material at backside of cavities and hide the small defects. This gate is applied for parts with excellent visual appearance.
- Hot tip: this gate connects directly to sprue, and inject plastic form top side to molds. There is no materials waste in runner system. It is ideal for large scale production, but left a visible dimple at the injection point.
Mold Unit
The molds are just like the negative of parts geometries photograph, its geometry and surface texture are transferred to injection molded parts directly.
Usually, molds cost are the largest portion of injection molding start-up cost. For simple geometry and small volume production, the mold cost might be $2,000 to 5,000. For optimized molds and full-scale production, the mold cost will raise to $100,000, in reason of a high quality mold can produce thousands to hundreds of thousands parts with accurate tolerance.
Molds are CNC machined of aluminum or tool steel, then finished to required standard. Except negative of parts, molds also have other functional features, such as runner system, which facilitates melted plastic into molds, and internal water cooling channels, which speed up parts cooling.
Mold anatomy
The simplest mold is straight-pull mold, it usually consist of 2 halves: cavity (front side) and core (back side).
In most case, straight-pull molds are preferred in reason of its simple design and manufacture, this will keep the total cost low. There are some design restrictions of straight-pull molds: the parts must be 2D geometry on each side without overhangs.
Once require complex geometries in molds, we need retractable side-action cores or other inserts. Side- action cores are mobile components with top or bottom entrance to molds, which are applied to manufacture parts with overhangs. Because side-actions increase molds cost rapidly, so we should use ti sparingly.
Notice: almost 50% of injection molding cycle is cooling and solidification. So minimizing design thickness is key to speed up and reduce costs.
Mold sides
Injection molded parts have 2 sides, the A side, which face molds cavity, the B side, which face molds core. These 2 sides have different purposes.
The A side has better visual appearance, also called cosmetic side. It will be smooth or textured as your design specifications.
The B side contains the hidden structural elements, like bossed, ribs, snap-fits. It is also called functional side, and has rougher finishes and visible marks of ejector pins.
Ejector Unit
Ejector Unit contains the clamping and ejection system. This system has 2 functions, keep two mold parts shut during injection, and push molded parts out after solidification.
As there is no perfect alignment of 2 mold moving parts, this will create two common visible defects on injection molded part.
Parting line: it is on part side where two mold halves meet. It is caused by tiny misalignments and round edges of molds.
Ejector marks: it is visible on the hidden B-side of part. It is always created by ejector pins below molds surface.
Benefit of Injection Molding
High volume production
Injection molding is the most competitive manufacturing method for high volume plastic parts production. As the mold is set up in injection molding machine, then plastic parts can be produced at high speed with low cost. The minimum volume of injection molding is 500 units, at this point, the high initial cost of molds has less affection on unit price.
Wide range material
Most thermoplastic, some thermosets and silicone can be applied in injection molding, this provides a wide range of materials with diverse physical properties. Injection molded parts have excellent physical properties. These properties can be custom manufactured by additives like glass fibre or different pellets mixture like PC/ABS blends. In order to achieve required level of strength, stiffness or impact resistance.
High productivity
The injection molding cycle time is typical 15 to 60 seconds, which is determined by parts size and molds complexity. In addition, one mold can accommodate multiple parts and increase production capability in manufacturing process. This means thousands of plastic parts can be produced in each hour.
High tolerance
The injection molding process is high repeatable with high tolerance. As wear occurs to molds over time, the aluminum molds for pilot-run will last 5,000 to 10,000 cycles, while tool steel molds for full scale production can stand 100,000 cycles.
Injection molded parts have tolerance of ± 0.500 mm, in special requirement case, we also can reduce tolerance to ± 0.125mm.
Excellent visual appearance
Injection molding can produce finished parts with little extra finishing. The molds surface can be polished to high degree of mirror-like, or bead blasted to textured surface.
Limitation of Injection Molding
High cost of molds
The main restriction of injection molding in economy is high molds cost. As a custom mold need to be manufactured for each geometry, so the start-up costs are very high.
Costly design changes
Once molds are produced, design changes require a new mold manufacturing form scratch. In reason of this, the correct mold design is very important for injection molding.
Long lead time
Injection molding turnaround is between 6- 10 weeks, 4-6 weeks for mold manufacturing, 2-4 weeks for production and shipping. This time will increase accordingly once design changes are required.