CNC machines, such as lathes, mills, and routers, are comprised of several distinct parts. Among them, the spindle is a critical component that significantly affects the performance of the machine, ensuring that parts are produced accurately. Therefore, before deciding on the type of spindle to use, it is important to comprehend how it operates.
This article will explain what a CNC spindle is, how it works with machine tools, its functions, and the various kinds of spindles available.
What Is A CNC Spindle & How Does It Work?
The CNC spindle, also known as spindle drives, is the central shaft in the rotating axis of machine tools, but it can also refer to the entire rotary unit with its bearings and attachments. It receives input from the CNC controller to rotate on its axis, making it a critical part of a CNC machining center. The type of spindle determines the cutting speed and force, and a machine tool may have multiple spindles, with the largest being called the main spindle. There are various configurations and options available for spindles to meet different needs, such as lathe, milling, grinding, electric, low-, and high-speed spindles.
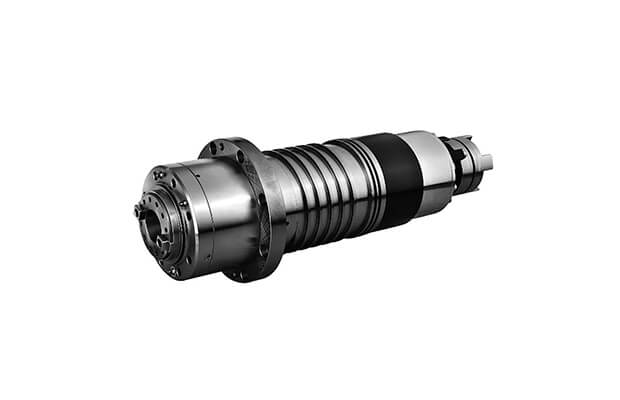

A spindle typically consists of a motor, a shaft holding the tool, and a taper for tool control. As it rotates on its axis, the spindle cuts, slices, and refines materials based on commands from a computer.
Components of A CNC Spindle
While there are many parts in spindles, a typical assembly consists of a rotating shaft, supported by a bearing system, and driven by an internal or external motor. The various components and subsystems are briefly described below.
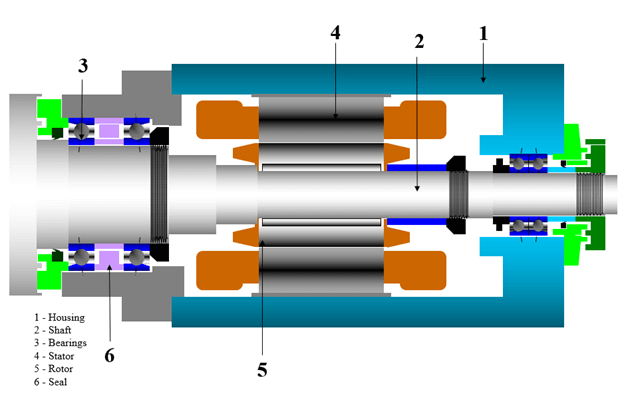
Spindle Motor
Each spindle’s drive system is determined based on the requirements of the application for speed, power, and stiffness, regardless of whether it is belt-driven, gear-driven, or made with an integral motor design.
Belt and gear-driven spindles are generally used when higher torque is needed and are powered by an external motor and pulley system, while integral motor designs are utilized at higher speeds and generate torque and power through the system where the stator and rotor are situated within the spindle housing.
Spindle Housing
The spindle housing can come in various designs, such as an integrated part of the machine, a block style, or a cartridge that is flange-mounted. Its primary purpose is to support the bearing arrangement on the shaft precisely and reduce vibration levels from the machining process. It provides several utility systems to the spindle, such as channels for lubrication of the bearings, air passages for internal pressure, and cooling jackets to minimize heat.
Shaft
The primary function of the shaft is to transfer rotational force from the drive system. It is secured by a set of bearings that facilitate its rotation along the spindle’s centerline. Spindle shafts are commonly hollow with a tapered end to accommodate a drawbar or tool retention mechanism.
Bearings
The lifespan of a spindle heavily relies on the bearing type used, which should be chosen based on the required speed, torque, and load. Angular contact ball bearings are usually used for high-speed units, while roller bearings are more suitable for higher stiffness and load capacity. The lubrication techniques, precision levels, and preload amount are adjusted according to the specific needs and circumstances of the application. The overall configuration is also considered to meet the demands of the required conditions.
Seals
Spindle failure caused by external contamination can be prevented by using seals to keep contaminants like swarf out of the bearings. The two main seal types are contact and non-contact seals.
- Contact seals are simple, with a lip that sits on the shaft, but they wear out over time due to rotational forces.
- Non-contact seals are made of fixed and rotating components that create a labyrinth to prevent contamination. They also allow for adequate protection against contaminants while keeping heat and wear low due to zero surface-to-surface contact. When choosing a seal type for a spindle design, the application criteria, spindle complexity, and housing space will determine which seal type to use.
Collet or Chuck
A collet or chuck in a CNC spindle is used to securely hold a cutting tool in place during machining operations. It is a mechanical device that grips the tool shank with high force and accuracy, allowing for precise and repeatable cuts.
Drawbar
The tool’s clamping mechanism is called the drawbar, which is made up of a rod with a set of springs that apply the required force to grip and release the tool. The force comes from a back-mounted actuating cylinder that operates through either hydraulics or pneumatics. At the front of the drawbar, there is a gripper that holds the tool in place when it is under load.
Types of CNC Spindles
A variety of shapes and sizes are available for CNC spindles. This part will classify them based on different parameters for easy identification.
Based on spindle orientation
- Vertical Spindles – In this type of spindle, the cutting tool is positioned vertically, with the axis of rotation perpendicular to the worktable. Vertical spindles are typically used in milling machines and drilling machines. They are also commonly used in industrial applications such as machining centers, where the workpiece is held stationary while the cutting tool is moved along various axes.
- Horizontal Spindles – In this type of spindle, the cutting tool is positioned horizontally, with the axis of rotation parallel to the worktable. Horizontal spindles are typically used in lathes, boring machines, and grinding machines. They are also used in some milling machines and machining centers. Horizontal spindles are known for their ability to achieve high cutting speeds and accuracy.
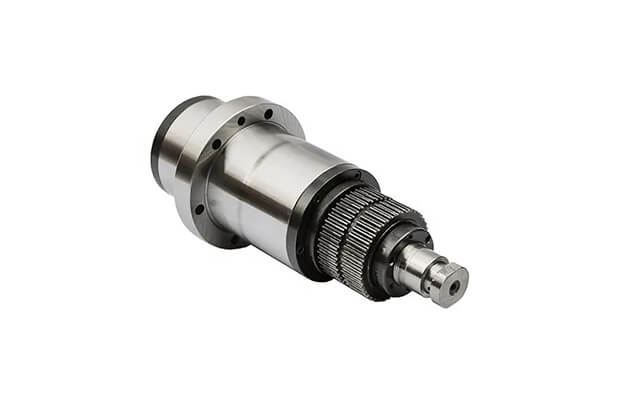
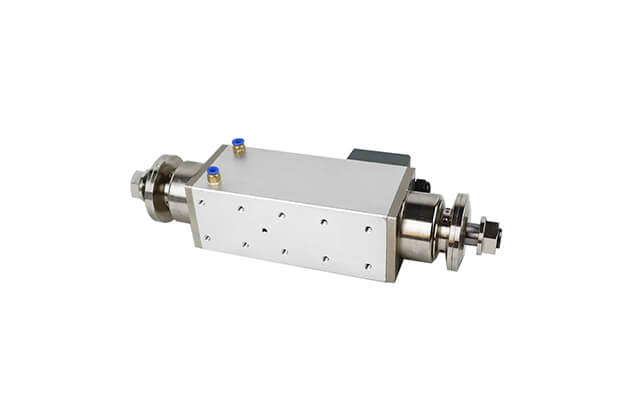


Based on tool holding mechanism
1. Collet Spindles – These spindles use a collet to hold the tool in place. The collet is tightened using a special tool or a wrench, which provides a strong grip on the tool. Collet spindles are commonly used in milling machines and routing machines.
2. Hydraulic Chucks – Hydraulic Chucks use hydraulic pressure to clamp the tool into place. These spindles are highly precise and ideal for high-speed machining. They are typically used in turning centers and grinding machines.
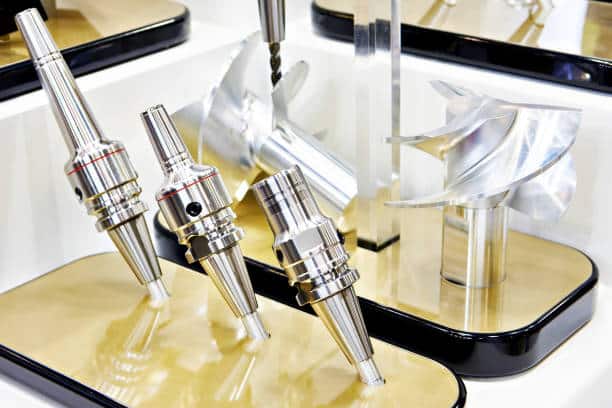

3. Shrink Fit Tool Holders – These spindles use heat to expand a special type of collet, which grips the tool tightly. The collet then shrinks as it cools down, thereby holding the tool in place. Shrink fit tool holders are highly accurate and provide excellent rigidity. These spindles are commonly used in machining centers.
4. Weldon Tool Holders – Weldon tool holders have a straight shank that is held in place by a set screw. They are commonly used in milling machines and are excellent at removing material quickly.
5. HSK Tool Holders – HSK (Hollow Shank Taper) tool holders use a conical interface to hold the tool in place, and they are highly accurate and rigid. HSK spindles are commonly used in high-speed machining and are ideal for applications that require high precision.
Based on power drive
- Belt-Driven Spindles – A belt-driven spindle is used to transmit power from the motor to the spindle. This system is relatively simple and affordable, making it a popular choice for CNC machines. The belt can be replaced easily if it wears out over time or if the application requires another type of belt. However, belt-driven spindles are limited in the amount of power they can deliver, which restricts their capability to heavier milling and cutting workloads.
- Direct-Drive Spindles – In a direct-drive spindle, the motor directly connects to the spindle shaft, providing more power and torque than in belt-driven spindles. This setup results in better accuracy, positioning, and stability, making it a popular choice for precision CNC machining operations. Direct-drive spindles require low maintenance and are durable in long-term use.
- Air Turbine Spindles – An air turbine spindle uses compressed air instead of electricity to drive its motor. This type of spindle is known for its high speed, accuracy, and low vibration. It offers precise and consistent results, especially during high-speed manufacturing processes, and can perform small cutters efficiently. However, they are expensive and can require extensive maintenance, including regular oil lubrication.
- Hybrid Spindles – A hybrid spindle combines two or more types of motor systems, usually a belt-driven or direct-drive spindle and an air turbine spindle. This configuration offers the advantages of all spindle types, resulting in higher speed, power, and torque, making them suitable for a wide variety of applications. The hybrid spindle design also allows for customization, allowing CNC machines to use a combination of spindle systems that best suit the user’s needs.
- Gear-driven Spindles – A gear-driven spindle is a type of spindle that uses gears to transmit power from the motor to the spinning part of a machine or tool. The gears are arranged in such a way that when the motor rotates the input gear, it drives the output gear that is mounted on the spindle shaft. The spindle shaft then rotates at the same speed as the output gear, which allows the tool to cut or shape the material. Gear-driven spindles provide a high torque output, which is essential for cutting through hard materials like metal. However, it may require more maintenance than other types of spindles due to the complexity of their design.
Functions of CNC Spindles
Spindle-containing machines are versatile tools that can be used for metalworking, woodworking, and creating and manufacturing CNC parts with different shapes. The chart below summarizes the functions spindles perform in the CNC machining process:
| Function | Description | Application |
| Milling | Available for a variety of milling tasks, including contouring, pocketing, slotting, and facing. They provide high accuracy and repeatability and can handle a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics to composites. | Aerospace parts, automotive components, and medical implants. |
| Drilling | Ideal for drilling tasks, as they provide high spindle speeds and torque to quickly and accurately drill holes of various diameters and depths. They can drill through a variety of materials, from soft woods to hard metals. | Precision drilling in circuit board production, metal fabrication, and other industries. |
| Routing | Used for routing tasks, such as cutting intricate shapes and designs in wood, plastic, and composite materials. They can produce smooth finishes and sharp corners and can handle complex 3D shapes with ease. | Cabinetry, furniture manufacturing, and signage production. |
| Grinding | Grinding surfaces, edges, and contours of various materials. They provide high accuracy and repeatability and can be used for both rough and finish grinding operations. | Tool and die making, mold making, and aerospace parts manufacturing. |
| Engraving | Creating intricate designs and text on a variety of materials, from metal to glass to stone. They can produce high-quality results with high precision and accuracy and can handle both shallow and deep engraving. | Jewelry making, gift items, and architectural signage. |

Benefits of Using CNC Spindles
CNC spindles offer a range of advantages over traditional machining techniques, including:
- Accuracy: CNC spindles are highly precision and precise, with the ability to cut and shape materials to extremely tight tolerances.
- Speed: High-speed machine spindles can work at high speeds, allowing for faster machining times and increased production efficiency.
- Consistency: CNC spindles can perform the same task repeatedly without any variations, ensuring consistent quality output.
- Versatility: CNC spindles can be used on a wide range of materials, from plastics to metals, and can perform a variety of cutting and shaping operations at high temperature.
- Automation: CNC spindles can be fully automated, reducing the need for operator intervention and increasing productivity.
- Cost-effective: CNC spindles can save money in the long run by reducing wastage, minimizing errors, and increasing production efficiency.
- Flexibility: CNC spindles can be configured in various ways, including multi-axis machining and tool changers, offering greater flexibility in manufacturing processes.
How to Choose the Right Spindle for Manufacturing
There are a broad of options available when you select a spindle for your CNC machine. To produce the exact results for your machining projects, you have to take account relevant factors carefully. Here, we summarize the main considerations for your reference.
Power and Speed
The power and speed of a spindle will determine how quickly and accurately it can cut through materials.
- Under 1500KW: more suitable for small-scale projects, especially for materials like wood and plastic.
- 1500KW – 3000KW: cutting and engraving of wood and plastics, while aluminum can be cut using spindles at 2200KW and above. These spindles are mostly used in standalone CNC machines.
- 3000KW and above: required for working with hard metals and stone, with mild steel processing possible at around 3000KW but stainless steel processing needing 7000KW or more.
Workpiece Materials
It’s vital to carefully evaluate the workpiece material and machining requirements to select the appropriate spindle for optimal performance in CNC machines.
- Compatibility: Materials such as wood, plastic, and soft metals require a lower powered spindle, while harder metals require a more powerful spindle.
- Hardness: If you are working with abrasive materials like metals, choose a spindle with high hardness and wear resistance. Otherwise, a spindle with lower hardness helps avoid damaging the workpiece.
- Density: Materials with high density require a spindle with a higher power output to effectively cut and shape them.
- Thickness: If the material is thin, a lower power spindle may be suitable, while thicker materials require a spindle with higher power output to achieve effective results.
Precision
The precision of a spindle refers to how accurately it can maintain the tool’s position while cutting. Higher precision is essential when working with more delicate materials or making intricate cuts.
Cooling Method
CNC spindles can be air-cooled or water-cooled. Air-cooled spindles are typically less expensive and simpler to set up, but they may not be as effective at dissipating heat during long periods of use. Water-cooled spindles, on the other hand, are generally more efficient at heat dissipation but can be more expensive and require specialized plumbing.
Compatibility
The spindle’s compatibility with your machine is essential. Check the specific requirements of your CNC machine compared to the spindle you intend to purchase.
AC vs DC Currents
CNC spindles are designed to operate with either AC or DC current. AC currents are typically used in high-power applications, such as industrial machines. DC currents are more suitable for small-scale projects.
Size
To choose the proper size of a spindle for your CNC machine, you have to consider several key factors in the following:
- The machine’s horsepower: Heavy-duty machines require a spindle with a higher horsepower rating, while lighter machines such as desktop machines can work well with a smaller, more compact spindle.
- The type of cut: If you’re cutting through heavy materials such as wood, metal or plastics, you will need a spindle with a larger size to handle the material.
- The project scale: The scale of your project requires spindles with either small or large capacities to accommodate.
- The collet size: Choose a spindle size that matches the collet size of your machine to ensure that it fits properly.
Conclusion
The spindle is a critical component in a CNC machine to automate and control the cutting, drilling, and routing processes. It enables operators to achieve complex designs and finishes on the workpiece with greater ease and speed. Therefore, understanding the importance of the spindle is crucial to achieving optimal results and improve the efficiency of the CNC machining process.
Work with Runsom – A One-Stop CNC Machining Services Supplier
Simply having a basic understanding of the CNC spindle is not enough to finish your projects perfectly, as many other challenges and difficulties are needing to handle. Instead, why not turn to Runsom, a one-stop service provider with extensive experience in CNC machining? Our knowledgeable technicians are well-versed in various machine tools and machining processes, and they will work closely with you to identify the most cost-effective solution. Require an instant quote today!
Other Articles You May be Interested in:





