Milling and turning with a CNC machine could seem precisely the same to someone unfamiliar with the process. After all, they seem to be extremely similar procedures and produce outputs that are comparable to one another.
However, suppose you are aware of the key distinctions between CNC milling and turning. In that case, you will be able to choose the process that most closely matches the specifications of your undertaking, which might end up saving you a significant amount of time and money.
What is CNC Machining?
This article will first examine the umbrella word often used to refer to CNC turning and milling before delving into how these two processes vary. Customers may request CNC machining services, and it is the manufacturer’s responsibility to choose the most appropriate approach, given those specifications.
Computer Numerical Control, or CNC for short, refers to the process of entering commands into a machine to have that machine subsequently control the lathes, mills, grinders, and routers. The excess scrap metal is subsequently eliminated, leaving a finished product that precisely meets all of the part’s requirements.
Difference between CNC Milling & Turning
The answer, in a nutshell, is that CNC milling makes use of a rotating tool, whereas CNC turning makes its cuts with the assistance of a rotating part.
Therefore, the two make use of a variety of various methods while creating a component. Turning is often used for the production of cylindrical pieces such as shafts, in contrast to milling, which carves away surplus material from metal blocks in order to produce more complicated parts.
Here are a few more differences between CNC turning and milling:
- Tool Features: The tool for CNC turning is single-point, while the tool for milling is multi-point.
- Uses: CNC milling is more suitable for machining irregular and flat surfaces, while CNC turning is better suited for processing conical or cylindrical surfaces.
- Cutting: CNC turning involves continuous cutting, keeping the tool approaching the workpiece. CNC milling adopts intermittent cutting, and the cutting teeth are constantly in contact with and disengaged from the raw material.
- Chips: CNC milling always makes discrete chips while CNC turning can produce discrete, continuous, and scattered chips.
Key differences between the two manufacturing processes are listed in the following table for easy reference.
| Features | CNC Milling | CNC Turning |
| Function mechanism | The stationary workpiece is processed by a rotating cutting tool moving linearly to remove materials and make wanted shapes. | The rotating workpiece is cut by a stationary cutting tool to form desired shapes. |
| Operations | Angular miling, plain milling, and face milling. | Taper turning, external grooving, straight turning, threading, drilling, knurling, and boring. |
| Shapes generated | Symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes. | Axisymmetric shapes such as cylinders, disks, polygons, hexagons, and cones. |
| Materials available | Metal, plastic, wood, and composites. | Plastic, metal, or wood. |
Now let’s have a look at each process in more detail.
What is CNC Milling?
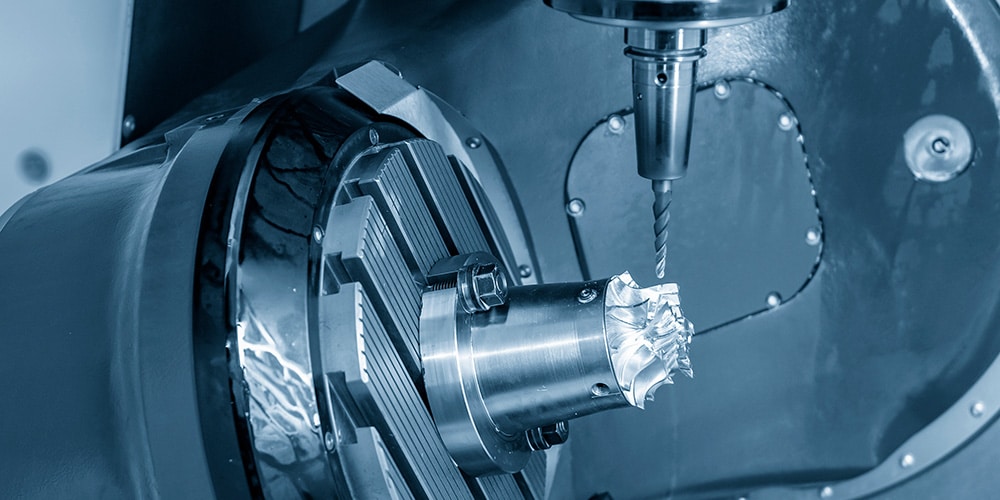
Let’s begin with the milling process. First of all, there are more conventional 3-axis CNC milling machines. The X, Y, and Z axes are the three different directions that the cutting tool may travel in.
Even though this has certain restrictions on the geometry of the pieces, it is sufficient for finishing the majority of the projects that need milling. Different types of milling, such as end milling, hollow milling, face milling, and so on, are all possible thanks to the large variety of milling tools.
The multi-axis milling process, including the 4-axis milling, allows for the movement of the work table and the tool. This adds a further degree of flexibility. The most popular of these is the 5-axis milling machine, which can generate almost anything that can be milled and is capable of doing it at an extremely high level of precision.
The overall dimensions of the completed portion are often less than those of the original block, which has dimensions that are typically bigger. As a result, precise milling is attainable for each and every side. Because the tolerances are so stringent, it should not be difficult to get excellent surface quality.
How about the Production Capacity of CNC Milling?
CNC milling can be used for both high or low volume production runs. CNC mills are commonly found in heavy industrial facilities as well as small machine shops, and even high-end science laboratories. The milling process can handle almost every material, although some milling machines may be specialized (for example, metal versus wood milling machines).
What Makes A CNC Milling Machine Unique?
The workpiece is generally fixed in place on a bed in a milling machine. Relying on the machine configuration, the bed may travel along the X, Y, or Z axes, but the workpiece itself is stationary. Milling machines typically employ rotating cutting tools mounted along a horizontal or vertical axis.
A milling machine can drill or bore a hole, or repeatedly on a workpiece, which can achieve the effect of grinding.
What is CNC Turning?
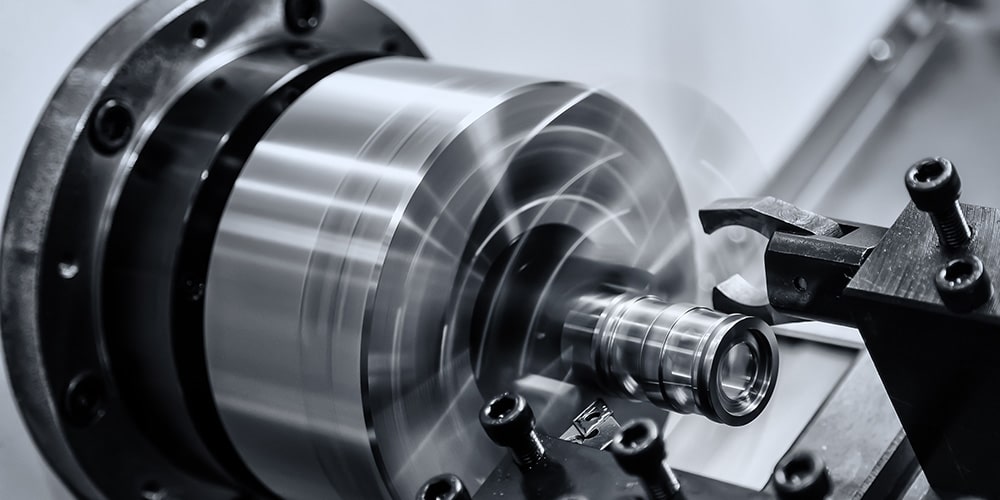

As was mentioned earlier, the primary use for CNC turning operations is the production of cylindrical components. These might be shafts, conical forms, specialized hollow tubes, or any other kind of item that is axially symmetric.
The creation of cylindrical pieces may also be accomplished using 5-axis machining; however, turning is simply a more efficient process, and the hourly cost for these tools is cheaper.
The raw material, which is typically a circular bar, is secured in place by the chuck. The chuck rotates at high speeds alongside the spindle while the machine works. The max speed, measured in RPM, varies from machine to machine.
The turret that holds the single-point cutting tool is mounted to the machine. While the functional piece is rotating, the turret may travel to and from it, allowing the cutting tools to come into proximity with the metal.
Because it is so accurate, this kind of machining makes it feasible to achieve very close tolerances. Because it is simpler to achieve the needed precision on the shaft using the hole-basis system, limits and fits often go along with that particular system.
How Does CNC Turning Suit Modern Manufacturing?
CNC turning is better suited for cutting cylindrical or asymmetrical parts. It can also be used for the removal of materials in the same shape – boring, drilling, or threading. CNC lathes have the capability of creating everything from large shafts to miniature screws.
What Makes A CNC Lathe Special?
CNC lathes, also called CNC turning machines, rotate the part itself while cutting tools keep stationary. This cutting operation allows the CNC lathe to handle designs that would be impossible with a traditional CNC mill. The tool setup is also different; the stability provided by mounting the workpiece on a rotating spindle between the headstock and tailstock enables the turning center to run fixed cutting tools. Different cuts and finishes tools can be realized by tools with angled heads and bits.
Live tooling is a powered cutting tool available for CNC turning centers, although it is more frequently used in CNC mills.
Advantages of CNC Milling
Manufacturers and prototype firms stand to benefit in a variety of ways from using CNC mills. In contrast to lathes, milling machines are multipurpose tools that may be used to fashion various forms. In addition, several operations, such as roughing and end-milling, call for different types of cutting tools, which are available in a wide range of CNC milling.
Mills are production facilities in their own right, but they also have applications in post-machining. For instance, they may be employed to add details to components that have been turned, 3D-printed, or molded.
Since CNC milling does not need tooling, it is quick, repeatable, and cost-effective, even when producing just a small number of parts. Consequently, it is included in the category of manufacturing services as well as rapid prototyping services.
Advantages of CNC Turning
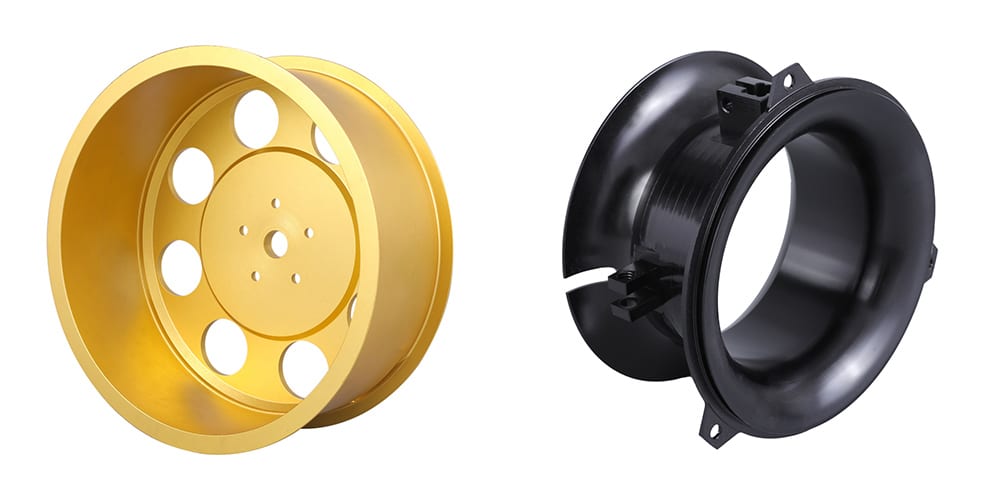

The capability of CNC turning to manufacture cylindrical profiles is the primary benefit of using this technique. When employing other types of CNC machining services, such as CNC milling or CNC routing, it is considerably more difficult to obtain exact roundness in the finished product.
CNC turning is also exceptionally accurate, which renders it a beneficial method for boring holes of specific dimensions with predetermined tolerances.
It is possible to merge CNC milling and CNC turning to gain both operations’ advantages at once. The vast majority of the time, CNC turning comes first, allowing the machinist to mill additional (asymmetrical) features on the item.
What Should You Use: CNC Turning or Milling?
CNC milling is most useful for surface work such as grinding and cutting, as well as symmetric and angular geometry when it comes to component design. There are two distinct subtypes of CNC milling machines: horizontal and vertical milling machines. Each subtype has its own set of distinguishing characteristics. Vertical mills that are well-constructed are surprisingly adaptable, which makes them perfect for many sorts of precision work. Horizontal mills, as well as vertical mills that are heavier and suited for production levels, are often planned and constructed for high-end, high-volume manufacturing runs. Milling machines designed for the industry are present in almost all of today’s factories and production facilities.
The CNC turning process, on the other hand, lends itself particularly well to prototype and low-volume manufacturing in general. CNC turning is very effective for producing asymmetrical and round shapes. Turning centers controlled by a CNC may also be used to mass manufacture certain specialized components, like screws and bolts, for example.
Finally, there are situations where you are not required to choose, and CNC milling-turning centers combine the two processes into a single manufacturing equipment for increased efficiency.
Work with Runsom for Your CNC Machining Projects
Whether you are looking for CNC milling, CNC turning, or any other precision machining services, you need to find a manufacturer you can trust. That is the access to receive high-quality components at a competitive price for you.
This is where Runsom Precision can help. With over 10 years of experience delivering industry-leading precision engineered components, we are specialists in CNC milling, CNC turning, Swiss CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal fabrication, rapid prototyping, die casting services, and other services such as secondary processing operations, packaging, assembly, and shipping, building long-term cooperative relationships with our customers who count on us time and time again.
We also guarantee you a fast quote and can process various parts of all shapes and sizes – as long as you need, we can do it. To find out how Runsom helps you with your crucial demands, fill out a quote online or directly contact a member of our team today.
Other Articles You May be Interested in: